
ELEMENTARY CHINESE
Chinese Characters
汉字
Volume I
April 1977
Revised December 1977
DEFENSE LANGUAGE INSTITUTE FOREIGN LANGUAGE CENTER
Preface
This sequel to Chinese Characters 工 is based on the PRC text Elementary Chinese’ and is designed to increase your reading vocabulary to 821 characters through the introduction of 521 new characters. Since Elementary Chinese represents current usage in the People:s Republic, it is to be expected that many words and their usages will not have been introduced elsewhere in this course; thus, you will need to learn not only the 521 new characters in this volume, but many new terms and their applications as well. At the same time, this inconvenience should be more than compensated for by the rewards of being able to read Chinese as it is used in the PRC today.
Design of this b?ok- Since Elementary Chinese was designed as a text of spoken Chinese, using it as a reading text presents some problems. First, many of the characters and words considered new vocabulary in the original EC are already familiar to you from CCI, Speak Chinese, and~Chinese Dialogues, Thus it was necessary to restructure the lesson introductions, limiting vocabulary to unfamiliar words and characters. Second, the resulting learning load was very uneven--too few items in one lesson and too many in the next. So the next step was to regroup vocabulary and lessons with the goal in mind of keeping as near as possible to 15 characters per lesson while preserving EC lessons intact. In some of the later lessons of EC, vocabulary far exceeds optimum limits for a two-day lesson eycle, and it may be necessary to spend more time on these lessons.
Meaning of symbols .
Parentheses around characters following the main entry indicate "long formsn or alternate forms of the character. (You are not required to learn these.)
请你黑y也来
Parentheses around a character or characters in a subentry or usage example indicate that the character(s) has not yet been introduced, and need not be learned at this point.
shēng(r) shūjià(zi) gaihao(le)
Parentheses around a syllable or syllables of Pinyin indicate that the enclosed is optional to the meaning of the term or phrase.
róngyi*
「不知神 bùzhibùjué
An asterisk following the Pinyin marks a word that has been introduced earlier in the course, or a phrase whose components are familiar.
Large brackets surrounding an entire entry or entries indicate that the enclosed is provided for your interest; such items are intended to enhance your understanding of character meanings and word building, but they need not be committed to memory.
A: without realizing it, before one knows it
Ijsage Examples. In most cases, new terms or expressions are followed by one or more sentences illustrating the usage of the item. Using a sheet of scratch paper, translate each example as you come to it. Then turn to the end of the vocabulary section and compare your translation with the version in the book. The models we have provided are merely-suggested renderings, but your translation should come fairly close to ours. Always be as accurate and literal (that is, faithful to the sense, feeling, and structure of the original) as good English permits.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
|
Lesson 9 Grammar Notes 9A (EC 35) 9B (EC 36) |
96 100 101 104 |
|
Lesson 10 |
108 |
|
Grammar Notes |
112 |
|
10A (EC 37) |
113 |
|
Lesson 11 |
117 |
|
Grammar Notes |
122 |
|
11A (EC 38) |
123 |
|
Lesson 12 |
127 |
|
Grammar Notes |
130 |
|
12A (EC 39) |
132 |
|
12B (EC 40) |
136 |
|
Lesson 13 |
139 |
|
Grammar Notes |
144 |
|
13A (EC 41) |
146 |
|
Lesson 14 |
149 |
|
Grammar Notes |
154 |
|
14A (EC 42) |
155 |
|
14B (EC 43) |
158 |
|
Lesson 15 |
163 |
|
Grammar Notes |
167 |
|
15A (EC 44) |
169 |
|
Lesson 16 |
174 |
|
Grammar Notes |
182 |
|
16A (EC 45) |
184 |
|
16B (EC 46) |
189 |
|
Appendix I |
192 |
|
Appendix II |
210 |
|
Appendix III |
229 |

Mao Zhǔxí huìjian Jixīngé
GuówùqTng
Chairman Mao meets Secretary of State Kissinger
Lesson 1
New Words with Old Characters
a. 孑 benzi N: notebook, exercise book
New Characters and Words
1.师询)shī
N: teacher; (military) division
4.吗
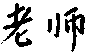
tā
nin
ma
laoshi
老弹为什么哭呢?
N: teacher
N: she
N: you (polite form)
P: (question particle)
5,和 he CV: and, with (like $艮)
6 .钢脚)gang
铜嵬 gǎngbí*
7. qiān
qiānbi*
N: steel
N: pen
N: lead
N: pencil
8.汉(漠)hàn
BF: China, Chinese (from the Han Dynasty--206 B.C. to 220 A.D.)
N: Chinese character(s)
9.
xi
BF: review, practice, study (again)
xuexi
V/N: study
10.
)11
BP: history
11.
shi
BF: history
lìshi
N: history
12.
kè
N: class period (M: jié 节); course (M: mén 门)
M: lesson
shàngkè*
xiàkè*
dìyíkè*
VO; go to class, hold class
VO: get out of class, dismiss class
lesson one, the first lesson
kèwén N: text (of a lesson)
13.祠 c1(r) N: word, term, expression (vs.冬,
single character)
« 'áì shèngcí N: new word(s), vocabulary (of a
£,」— lesson)
14.英
yīng
yīngguo* yīngwén*
BF: sublime, noble, eminent; used in transliterating
N: England
N: English (language)
Translations of the Usage Examples
a. Which student didn't have a notebook?
1. Why is the teacher crying?
5. Why don't you go with her!
8. Is it okay to use pens and pencils to write Chinese?
9. When you study Chinese characters, the teacher is very-important.
11. China has a 5000-year history.
12. Why doesn1t lesson 53 have any text?
This course is11tt too tough.
13. Ifve already forgotten the vocab from that lesson.

课外学习。
语法 Yùfá Grammar
1) In a sentence of the pattern "A 是 B", “是"is pronounced in the neutral tone "shi”. If pronounced in the 4th tone, “是" implies emphasis: "A is B”.
2) The interrogative particle 口吗》is put at the end of a declarative sentence to make it a question, e.g.
他是老师吗?
3) The Chinese personal pronoun in 3rd person shows no difference in gender, but the written form has differentiated into 他, 她 and 它,all pronounced "tā”.
1)都 and 也 both are adverbs,都 in a sentence shows that the word or phrase before comprises the entire of what it stands for. When 都 and 也 are used together,也 precedes 都.e.g.
我们都是学生。
你是老师,她也是老师。
他们是学生,我们也都是学生。
2) The suffix 们 is put after a singular personal pronoun or a noun denoting person to show plural number. Other nouns cannot take 们,so we can't say 书们,报们,etc.
If the context is quite obvious that the noun is in plural number, 们is not used, e.g.他们是老师.and we do not say他们是老师们.
一,范句 Fànjù Models
㈠
L我是 学生。
2.
他是老师。
3.
这是书。
4.
那是本子。
(二)
5.
她不是老师,是学生。
6.
那不是本子,那是书。
7
这是本子,不是书。
(三)
8
.你是学生 吗?
9.
他是老师吗?
10.
那是书吗?
11.
这是本子吗?
A:
你是 学生 吗?
B:
我是学生。
A:
他是 学生 吗?
B:
是学生。
A:
您是老师吗?
B,
,我不是老师,是学生。
A:
这是书吗?
B: 是。
A:
那是书吗?
B:
不是,那是本子。
Lesson IB (EC 14)
―、范句 Fànjù Models
(一)
我们都是学生。
他们都是老师吗?
他们都不是老师,都 是 学生。
(二)
那是书,这也是书。
我是学生,他也是 学生, 我们都是学生。
他们都是 学生,我们 也 都是 学生。
(一)
我是学生,你是学生,他也 是 学生。我们 都 是学生。我们 都不.是老师。
你们 是 学生, 他们 也是 学生, 你们和他们都是学生。她们不 是学生,是老师。
(二)
L这是书,那也是书。
2.
那是本子,这也是本子。
3.
这是钢笔,那也是钢笔。
4.
那是铅笔,这也是铅笔。
5.
这不是报,那也不是报。
6.
那不是纸,这也不是纸。
Lesson 1C (EC 15)
_,范句 Fànjù Models (-)
1.
老师教 中文。
2.
我们都学 中文。
3.
我们写汉字。
(二) 4.
我们有书,有本子,也有纸。
5.
他有铅笔,没有钢笔。
6.
他没有纸,我也没有纸,我们
都没有纸。
二,课文 Kèwén Text
我们是学生,我们都学习中文。 老师教我们中文,也教我们英文。 你们学历史,他们也学历史。你们和 他们都学历史。
她们念课文,你们写汉字。他们念 课文,也念 生词。我们 念课文,念 生词,也写汉字。
我们都有铅笔,也有钢笔。他们有 钢笔,没有铅笔。你们 有本子,也有 纸。我们都有本子,也都有纸.他们 都有本子,都没有纸。
New Characters and Words
|
1.练谶)liàn |
BF: |
practice, drill, train | ||
|
练2 |
liànxi |
V: |
practice, drill, train | |
|
我迁及嫌勺裸文0 | ||||
|
2..讲算)jiǎng |
V: |
explain; speak, talk | ||
|
jianghuà* |
VO: |
speak, talk (like ,鼠:名) | ||
|
3. |
fā |
V: |
issue, emit, send, shoot | |
|
4.音 |
yin |
N: |
sound, musical note | |
|
发者 |
fayin* |
VO: N: |
pronounce pronunciation | |
|
5.努 |
V nu |
BF: |
exert | |
|
6. |
lì |
BF: |
power, force, energy | |
|
努力 |
null |
VO: SV: A: |
do one1s best, work hard diligent 9 industrious with great effort, industriously | |
|
她陶力学习中文。 | ||||
|
7•题 |
tí |
N: |
topic, problem | |
|
问题 |
wèntí* |
N: |
problem, question | |
|
题⑻ |
tímu* |
N: |
topic, theme, title | |
|
8. |
dá |
BF: |
answer, reply, respond | |
|
仞容 |
huídá* |
v/n: |
answer | |
|
9. |
zhù |
BF: |
concentrate, fix (one1s eyes or mind) upon | |
|
浮卷 |
zhùyì* |
VO: V: |
pay attention pay attention to | |
|
你得多注态发者. | ||||
零 ling
Nu: zero
BF: fragment., ffaction, part
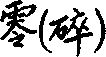
língqián* língsuì*
N: small change
SV: sundry, miscellaneous
17.
yù
BF: beforehand, pre-
11.
)zá
BF: random, miscellaneous
|
12. |
Io) zhì |
BF: |
remember, record; written record | |
|
乳公 |
zázhì* |
N: |
magazine, periodical | |
|
13.枝 |
zhī |
M: |
long thin object | |
|
一 |
•权笔 |
yìzhí bl* |
a pen | |
|
14.薄 |
báo |
SV: |
thin \. | |
|
15.厚 |
hòu |
SV: |
thick | |
|
16.复侬、fù 匐 |
BF: |
return, repeat, review, revive, restore, renew; multiple, complex | ||
|
复杂 |
fùzá* |
SV: |
complicated, complex | |
|
复习 |
fùxí |
V: |
review | |
|
我优先复m又五深0 | ||||
18.语 yu
女得 yīngyu hànyù
BF: language
N: English, the English language N: Chinese, the Chinese language N: grammar
Translations of the Usage Examples
1. I haven1t practiced the text yet.
6. She1s working hard to learn Chinese.
9. You need to pay more attention to pronunciation.
10. 43015.
3002.
16. First let1s review the first five lessons.
17. Be sure to prepare lesson 6 before coming to class tomorrow.
18. I don't think Chinese grammar is as complex as English.
语法 Yǔfa Grammar
1) Some verbs may take 2 objects with the indirect object preceding the direct object, e.g.
他教我们法文。
2) Besides nouns and pronouns, adjectives, verbs, etc. can also be used as objects, e.g.
我们练习听,也练习说。
我们练习说中文。
3)"不"used in front of a verb shows pure negation or will, and has nothing to do with tense, e.g.
她不会英文。
他不念课文。
("He does not read the text.v or tfHe would not read the text.
4)“不"is usually pronounced in the 4th tone, but when it is followed by another 4th tone, it's changed into the 2nd tone:
木会,木问,木是
1) Numeration The decimal system is used for numeration in Chinese.
一 二 三 四 五 六 七 八 九 十
十一十二十三..........................................二十
二 H-- 二十二.............................................一百
一百零一.........二百■一~b.........五百九十九......一千
一千零一……一千零十五……
……一干二百七十六……一千八百零二……二千
2)“几"and "多少" are interrogatives for numbers. If one asks about a number from 1 to 10, he uses "几"多少"can be used for any number, e.g.
这是几?
这是二。
那是多少?
那是一。
那是二十四。
3) Change of Tones of "一":
(1) . When standing by itself, or at the units or tens of numbers, "一"is pronounced in the 1st tone:"那是一"(Nà shi yi), “二百一十一” (èrbài yī shi yi).
(2) When “一" precedes a 4th tone or a neutral tone changed from a 4th tone, it is pronounced in the 2nd tone:"一课(y!kè one lesson),"一个“(yíg6 one). "—“ is pronounced in the 4th tone when followed by the other tones; “一百”(yib出)“一千''(ylqiWn) “一本” (yìběn).
(3) As an ordinal number, “一" is always pronounced in the first tone: "一月”(yīyuè January).
1) In modern Chinese a numeral cannot be put immediately before a noun and there must be a measure word in between. Many nouns have their respective measure words and the measure word "个” is most extensively used. e.g.
一本书,三枝铅笔,四张纸,十五个学生
2) When an adjective is used as the predicate, an adverb of degree is usually put before it and "很"is the most frequently used. But here "很is very much weakened and has almost lost its function as an adverb of degree. In an alternative question one does not use 很e.g.
那本书很新。
那本书不新。
那本书新吗?
那本书新不新?(不能说“那本书很新 不很新? ”)
When an adjective alone is used as the predicate, it implies comparison. e.g.
那本书新,这本书旧。
这张纸白,那张纸不白。
Note: When an adjective is used as the predicate, no "是"is used.
1) In Chinese, an attributive always precedes what it qualifies. When a personal pronoun or a noun is used in the genitive, it generally takes the structural particle "的e.g.
老师的画报,我的书

2) An alternative question is formed by joining together the aR firmative and the negative forms of the main element of the predicate, e.g.
你去不去?
这本书好不好?
If the verb takes an object, there are two possible ways to make an alternative question:
他是不是老师? 他是老师不是?
你会不会中文? 你会中文不会?
他们有没有英文书?,他们有英文书没有?
Lesson 2A (EC 16)
—,范句 Fànjù Models
(一)
老师教他们中文。
学生问老师问题。
她教我们历史。
(二)
我不念生词,我念课文。
他不教你们法文,教你们英文。
学生都会法文,却不会中文。
二、课文 Kèwén Text
老师教中文。
2.
老师
3.
我们
教我们中文。
会英文和法文。
4.
我们
5.
老师
学习中文。
说中文,我们注意听。
6.
老师
7.
我们
8.
老师
9.
我们 10.
老师 11.
我们 12.
老师
13.
我们 14.
老师
15.
我们 16.
我们
问问题,我们回答。
练习听,也练习说。
讲 生词,也讲课文。
念课文和生词。
教我们发音。
练习发音。
教我们汉字。
写汉字。
问我们问题。
回答问题。
都努力学习。
Lesson 2B (EC 17)
词组和范句 Cízǔ hé fànjù Word Groups and Models
(-)
二十」 三十二 四十三
一一百一六十五,
二百一十四 五百七十六 八百二(十) 五百零四 八百零九 一千三百零六 一千零五十八 一千九百七十一
(二)
这是几?
是十。
那是十几?
那是十二。
那是多少?
三百二十一。
© 二、课文 Kèwén Text
1.
这是几十?
是 二十。 一一一一…2. ......... ...........一一一,. ..........
这是三十几?
=+一1
3
4.
.那是二百几?
是一百甲(十)o
二百九十六。1
1、一 ” “ ...... ■.;, - 5". . ■■ —,y "3.
是七。
4"一
是二十八。
是 六百 五(十)。
... ■, 一,
一千零四。
Lesson 2C (EC 18) (Review)
一、句子 Jùzi Sentences
(-)
|
老师 |
教 |
中文英文法文 发音 汉字 历史 |
|
我 |
学(学习) | |
|
我 |
说 |
中文英文法文 |
|
他 |
会 | |
|
学生 |
念 |
,课文 生词 |
|
老师 |
讲 | |
|
他 |
写 |
汉字 |
|
老师 |
问 |
问题 |
|
学生 |
回答 | |
|
他 |
练习 |
发音汉字听说写 |
(二)
|
我(们) 你(们) 他(们) 她(们) |
(不)是 |
学生 老师 |
|
这 那 |
书 报 纸 本子 钢笔 铅笔 |
(三)
|
我(们) 你(们) 他(们) 她(们) |
有 |
书 本子 报 纸 钢笔 铅笔 |
(四)
|
他 |
(不) |
学 教 |
荚文 |
|
会 |
(五)
|
他 老师 |
(不)教 |
你们 我们 他们 |
中文 |
(六)
|
这是书吗? |
(这)是书。 |
(这)不是书。 |
|
你学中文吗? 老师教你们 中文吗? |
(我)学中文。 (老师)教我 们中文。 |
(我)不学中文。 (老师)不教我 们中文。 |
|
你有书吗? |
(我)有书。 |
(我)没有书。 |
(七)
|
这是几? |
123456789 |
|
这是十几? |
11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
|
这是几十? |
20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 |
|
这是几十几? |
21 22 23 34 35 36 47 48 59 62 73 84 95 99 |
|
这是几百? |
100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 |
|
这是多少? |
1 2 5 12 26 38 41 52 73 84 96 100 |
二、课文.Kèwén Text
L我们是学生。
2•我们学习。
3-我们会英文,不会中文。
4我们都学中文。
5-我们都努力学习。
6-我们念课文,也念生词。
7.老师讲,学生都注意听。
8.老师问我们问题,我们回答。
,我们练习发音。
©我们练习听,练习说,也练习写。
学生学中文。
12.你学法文,他学英文。
13.我学中文,他也学中文。
14.我和他都学历史。
6我教你中文,你教我英文。
Lesson 2D (EC 19)
一、词组和范句 Cízù hé fànjù Word Groups and Models
I1)
L 一本书 这本书
2 .'■个本子--那个本子
3 .一枝钢笔一那枝钢笔
4 一枝铅笔——这枝铅笔
5 .三张报一这三张报
6 .十张纸一一那十张纸
(二)
7 .这本书很新。
8 .这枝铅笔很好。
9 .这个本子很大。
(三)
■; Í-
10 .这本书不新。
11•这枝铅笔不好。
12.那个本子不大。
㈣
13.这是几本书?
14.那是多少(张)纸?
... .)■,
15.你有几枝钢笔?
16.他有多少(本)画报?
: . .. ■ . .. .「: 1 --..
㈤
17.这本书新吗?
18.这枝铅笔好吗?
19.那个本子大吗?
二,课文 Kèwén Text ㈠
1 .这是 •—本书,那是三个
本子。
2 .这是一张报,那是十张
纸。
3•这是一枝铅笔 和 钢笔。
一枝
四本
4.那是一本杂志 和 画报。
5.他有一本书和三个本子°
(二)
6•我有,一本书。
7-这本书很新,这本书很好。
8•这是杂志,那也是杂志。
9 .这本杂志新,那本杂志旧。
10 .这本画报新,那本画报不 新。
11 .这是十张纸,那 血是 十张纸。
12 .这十张纸很白,那 十张 纸也很白。
13 .这三个 本子 大,那 四个 本子小。
Lesson 2E (EC 20)
—> 词组和范句 Cízú he fànjù Word Groups and Models
|
1. |
我 |
(一) | |
|
的 |
书 | ||
|
2. |
你们 |
的 |
本子 |
|
3. |
他 |
的 |
钢笔 |
|
4. |
她们 |
的 |
铅笔 |
|
5. |
老师 |
的 |
钢笔 |
|
6. |
学生 |
的 |
画报 |
|
7. |
中文 |
书 | |
|
8. |
法文 |
报 | |
|
9. |
英文 |
杂志 | |
|
10. |
新 |
书 | |
|
11. |
旧 |
报 | |
|
12. |
白 |
纸 | |
(二)
13.这是不是书?
(这是书不是?)
14.这是不是你的书? (这是你的书不是?)
15.这是不是中文书? (这是中文书不是?)
16.这是不是新书? (这是新书不是?)
(三)
17.这本书新不新?
18.这本中文书好不好?
19.你的中文书多不多?
20.这课课文长不长?
21.那课课文难不难?
二、课文 Kèwén Text
(一)
这是我的书。那是他的书。他 的书很多,我的书也很多。我们的 书都很多。我们的英文书多,中文书 少。这本中文书薄,那本中文书厚。
那不是老师的本子,那是学生的 本子。我们都有本子。我们的本子都 很好。我们每天都作练习。
(二)
我们每天都
学习一课课文。这课
课文长,那课课文短。短课文容易, 长课文也不难c 我每天复习旧课,也预习新课, 我预习新课的生词、课文和语法。
New Words with Old Characters
a.工 彳乍 gongzuò V/N: work
New Characters and Words
1.析
xī
分材Mnxi
BF: split (wood, etc.); analyze
V: analyze
N-i analysis
2. jié BF: (bamboo) joint, juncture, festival;
section, segment, span; regulated, rhythmic; to regulate or restrict
M: class period
3. 辅 fǔ BF: help, support, aid
4. dao BF: lead, guide
辅导 fúdao V: coach
zhiháo*
BF: only
M: one of a pair
A: the best thing to do is, all one can do is...
yìzhī shou*
one hand
6.
min
BF: people; citizen
N: people
China Pictorial
7.班 ban
N/M:
shift; class; squad (of soldiers)
上缈,shàjigb'n* í xiàban*
VO:
VO:
go to work, go on duty, be at work or on duty
get off work, get off duty
这L指 zhèyibān*
this class (shift, squad)
shì
M:
BF:
number (#), day of the month
#13, the thirteenth of the month
room, office
N: classroom
jiān
M:
BF:
room
juncture, interstice; middle or midst of; among, between
臼间数篁 sijiān jiàoshì*
four classrooms
•午 wu
BF:
noon
上下中彳
彳 shàngwu* 牛 xiàwu* 斤 zhongwu*
wufan*
N:
N:
N:
N:
morning, forenoon
afternoon
noon
lunch, noon meal
bāngzhu*
BF:
assist, help
V:
N:
help, assist help, assistance
13.共 gong BF: altogether^ share
一yígòng* A: altogether, in all, all told
Translations of the Usage Examples
a. Where does she work?
1. The teacher analyzed the grammar of that sentence for us.
2. There are three hours (periods) of class a day.
4. Prof essor Wang of ten coaches us.
9. There arenT t enough desks here in our classroom.
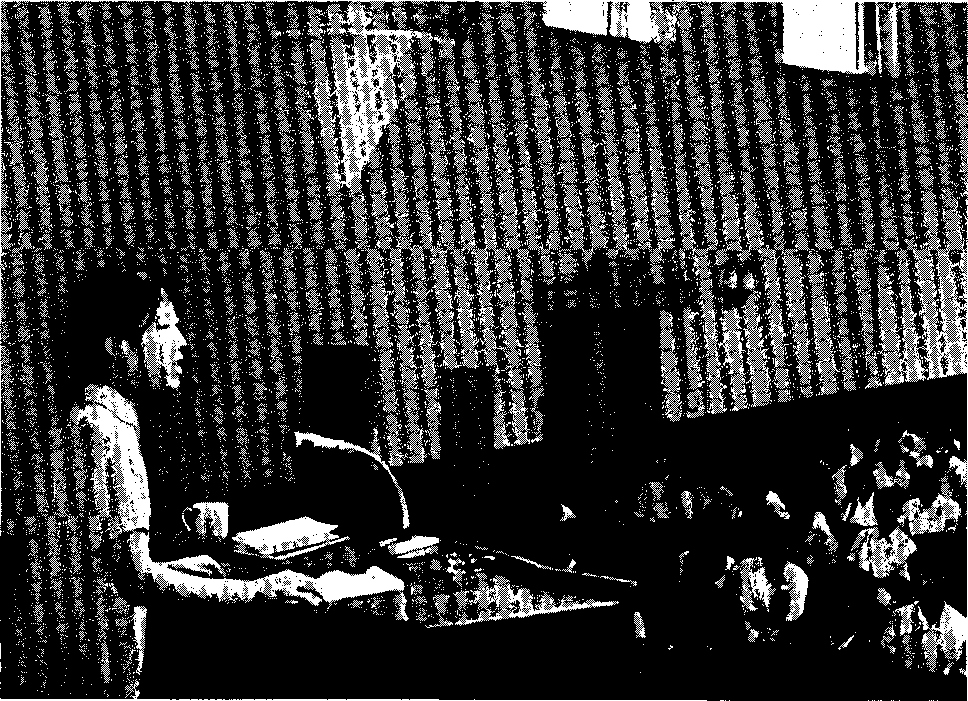
在辅导大会上
语法 Ytìfà Grammar x
1) In modem Chinese,"每"cannot be used immediately before a noun and a measure word must be put in between. Some nouns are also measure words and so do not take a measure word, e, g. “每天”,"每课”(every lesson, cp.。每节课"every class).
There are a few nouns which may take a measure word or not.e.g. a每人“,a每个人工
2) Sentences with,每“very often have "都" or a word or phrase denoting number to go with it (both may occur at the same time), e.g.
我们每天(都)有三节课。
老师问每个学生一个问题。
我们每个人都会英文。
每个学生都有中文书。
When “都” is used, it emphasizes that there is no exception to the case.
, ,, ; , i ■ ■..
1) Both“二”and«两"mean two, but they are not interchangeable:
(1) “二” is used as the ordinal number. e. g. 土 月(Febfuary), 第二课•
(2) As the last digit of a number larger than ten, «二》is used, e. g.十二,三十二,一百零二.
(3) Before «十” and “百”「二*s used. e. g.二十,二百,but before “千both «二” and “两" can be used:二千,两千.
(4) Before a measure word, “两” is used. e. g.两本书,两个: 人,两个月(two months, cp. 七月).But if the number before the measure word is larger than ten, the last digit must still be。二"and not “两乙 十二个生词,一百零二
■ . ■, ■ ■;,-1 一
个人Q
2) When”第一,第二,......力 come before a noun, there must
also be a measure word, e. g.,第一个问题" and not “第一问题”, but if- the noun is also a measure word, no measure word is used: “第二课” (lesson 2), “第二天汽
Lesson 3A (EC 21)
一、范旬 Fànjù Models
1.每个学生都有本子吗?
每个学生都有。
2.每人有几个本子?
每人有两个。
3.你们每天作练习吗?
我们每天作练习。
4.练习难不难?
不难,每课练习都不难。
5-你们都看中文报吗?
对了,我们每个 人 都 看
中文报。
二〉课文 Kèwén Text
A:你们现在学什么?
B:我们现在学中文。
A:以后 你们 每个 人 都 学 中文吗?
B:不,以后他们学法文,我们 学中文。
A:你们每天都有课吗?
B:对了,每天都有。
A:每天有几节课?
B:每天有三节。
A:课文难不难?
B:不难,每课课文都很容易。
A:老师也分析句子吗?
B:也分析°
A:老师常常辅导你们吗?
B:常常辅导我们。
A:你们看不看中文报?
B:看,我们每个人都看中文报。
A:你有 ,没有法文 '报?
B:没有,我只有中文报, 他们有法文报。
A:他们都看法文报吗?
B:对了,他们每个人:都看法文 报。他们只看法文报,不 看中文报。
A:你有中文画报没有?
B:有,我常常看《人民画报》。 你有没有《人民画报》?
A:我没有。
B:我给你一本《人民画报》, 好不好?
A:好!谢谢你!
Lesson 3B (EC 22) _、词组 Cízǔ Word Groups
L两本书
2-两本杂志 : ■ . 7
3 .两旅纸
4 .两枝钢笔
5 .两个本子
6 .两个句子一
7 .两个老师
8 -两课课文
9 .两节课
二,课文 Kèwén Text ㈠
「这是我们的教室。我们的 教室是 2 2 2 号(二二二号)。我们 班十二个人,毒在这间 教室 学习。
我们每天都有课。
上午有

两节课,下午 也有 两节 课。 今天上午第一节 学习 新课文, 第二节老师讲语法。下午 两节 课我们作一些练习。
每天晚上 我们 自己 复习 和 预习。老师 常常 来帮助我们。 第二十课 我 还 有 两个 问题, 今天晚上问老师。
(二)
他有两本中文画报,我有 十本中文 画报,我们一共 有 十二本中文画报。
第一课有十个生词,第二课有 十二个 生词, 两课 一共 有 二十二个生词。
New Words with Old characters
a.这里 zhèli (zhèli)
nàli (nàli)
c
náli
(nali)
N: here (like
这几)
N: there (like 对〉/L )
N: where (like 网。)
d.冢 jiǎ
huàjiā zuòjiā shixuéjiā
BF: (suffix for professionals and specialists)
N: painter, artist
N: writer
N: historian
N: grammarian
New Characters and Words
|
1J红 hong |
SV: |
red | |
|
2.蓝隆)lán |
SV: |
blue | |
|
3.黄 huáng |
SV: |
yellow, brown | |
|
4.绿儒)1Ù |
SV: |
green | |
|
5.同 tong |
SV: |
the same | |
|
V: |
in the same (class, group, etc) | ||
|
同学 |
tóngxué* |
VO: |
be a schoolmate of |
|
N: |
schoolmate | ||
|
同班 |
tóngbān* |
VO: N: |
be in the same class classmate |
|
同事 |
tóngshl* |
VO: |
be a colleague of |
|
N: |
colleague9 fellow worker | ||
|
38 | |||
I司日才16ngshi*
MA: at the same time
6.图(圈)tú
N:
diagram, chart, illustration
图节馆 túshūguan*
N:
library
N:
map
7.宿 sù
BF:
spend the night, stay (somewhere)
8」畲(拾)she
BF:
dwelling, hostel
舍* sùshè*
N:
dormitory
BF:
M:
framework, structure, shelf, rack (aircraft, machine, radio, etc.)
10.
12.
one aircraft
• • 、 • JL,
jiazi*
N:
N:
rack, shelf
bookshelf
床怫)chuáng
11.

chuángdān(zi)*
yìzhāng chuáng*
洛.g6ng
公共(匈隼 gonggòng qìchē*
.力、公 bàngòng*
N:
N:
BF:
N:
bed (M:个 or §长)
bed sheet
one bed
chair
chair (M:个"or 才6)
five chairs
BF: public; office, official duties
N: bus
VO: conduct official business
N: office
13.专(彖 zhu且n BF: concentrate, focus, specialize;
福) exclusive, specialized; specialty
zhuǎnjià N: specialist, expert ]
14.业O)y咨
BF: calling, trade, occupation, profession
zhuānyè
N: major field, specialty, profession
15.化 huà
BF: change, transform; transformation; civilization, culture
N: culture
N: chemistry Att: chemical
N: chemist
xīngxing
17,期一qī
18.或
huò
huòshi*
BF: star, heavenlybody
N: star(s) | ■ ■
■ : ■ ■ ■ . .. ; . .:.■'.
BF: period, time limit or duration
N: period (of time)
N: week ;■ ■■■..
BF : or
MA: or
19.者 zhě BF:
学作或 工
(as a V or VO suffix) they who, he who, one who; (suffix particle)
one who studies, scholar
one who works, worker
or
Translations of the Usage Examples
5. These two things arenT t the same.
12. My teacher1s office is #103.
13. Shers án expert on history (or a history specialist).
-.i"..
14. My specialty (or major) is history.
15. She studied chemistry in college.

在北京图书馆 jīng
语法 Yùfá Grammar、
1) A noun, personal pronoun or adjective plus ”的万 forms a nominal construction.e.g.
这本书是老师的。(老师的=老师的书) 这枝笔是我的。(我的=我的笔)
这本杂志是新的。(新的=新的杂志)
2) “多少 or “少" as an attributive must take "很"before it, e.g.
«很多书3 口。t”多书多的书“严很少人”,not“少人々I少的人汽
The word order of a question with an interrogative Dronoun is the same as that of a declarative sentence.e.g.
|
陈述句 |
疑问句 |
|
这本字典是张老师 的。 |
暨本字典是张老师的? |
|
这本字典是途的? | |
|
张老师有两本字典。 |
张老师有匹本字典? |
|
谑有两本字典? |
The order of a date is as follows:
一九六五年九月十五日(星期三)
Lesson 4A (EC
23)
—、范句 Fànjù
Models
1.这本
(-)
书是我的。
9.这本
2.那个
本子
他的。
10.
那本
杂志
3.这枝
钢笔
你的。
这枝
铅笔
4.
这本
画报
学生
的。
5.
那本
老师
的。
12.
这本
6.
这本
书是新的。
(这本
7.
这张
纸是白的。
13.
这本
画报
8.
那枝
铅笔是红的。
(这本
画报
14.
这枝
铅笔
(这枝
铅笔
二)
是我的。
是学生的。
是红的。
:)
不是你的?
你的不是?)
不是学生的?
一学生的不是?)
不是红的?
乏红的不是?)
二、,课文 Kèwén Text
(一)
这是我们的宿舍。我们的 宿舍有 两张 床、两张 桌子和 两把椅子,还有两个书架。左边 的书架是我的,右边的(书架) 是我同学的。
我们 .有很多书、本子' 和画报。
这个本子是薄的,那个本子是 厚的。这个薄本子是我的, 那个厚本子是中国朋友的。
法文画报是我们两个人的。
中文画报都是图书馆的。
(二)
1.他一共有十枝铅笔。
2-两枝(铅笔)是黄的。
3.两枝(铅笔)是蓝的。
小两枝(铅笔)是绿的。
5.四枝(铅笔)是红
的。
Lesson 4B (EC 24) (Review) 一、词组 Cízǔ Word Groups
(一)
|
两 四 这 那 |
本 |
书 ,杂志、画报, |
|
张 |
纸根桌子 | |
|
枝 |
钢笔铅笔 | |
|
把 |
椅子二. | |
|
课 |
课文生词语法 | |
|
节 |
课 | |
|
间 |
教室宿舍 | |
|
个 |
老师学生同学朋友 图书馆书架 汉字生词句子问题本子 |
(二)
|
这 |
两 |
本 |
书・•…•• |
|
张 |
纸……• | ||
|
那 |
三 |
个 |
学生…… |
(三)
|
我(们) 你(们), 他(们) 她(们) |
的 |
书' . 报 画报 | |
|
老师 学生 图书馆 | |||
|
中文•. |
杂志 | ||
|
英文 | |||
|
很多 |
铅笔 | ||
|
红 | |||
|
白 |
纸 | ||
|
长 |
句子 | ||
二、句子 Jùzǐ Sentences
㈠
|
这本书 |
很 |
新。 好。 厚。 |
(二)
|
这张报 |
(不)是 |
他 老师 中文 图书傕 旧 |
的。 |
(三)
|
1 |
这是书吗? 这是不是书? 这是书不是? |
这是书。 |
这不是书。 |
|
2 |
这本书是你的 吗? 这本书是不是 你的? 这本书是你的 不是? |
这本书是 我的。 |
这本书不是 我的。 |
|
3 |
你学中文吗? 你学不学中 文? 你学中文不 学? |
我学中文。 |
我不学中 文 |
|
4 |
老师教你们中 文吗? 老师教不教你 们中文? 老师教你们中 文不教? |
老师教我 们中文。 |
老师不教我 们中文。 |
|
5 |
你有中文书 吗? 你有没有中文 书? 你有中文书没 有? |
我有中文 书。 |
我没有中文 书。 |
|
6 |
这本书好吗? 这本书好不 好? |
这本书很 好。 |
这本书不 好。 |
三课文 Kèwén Text
(一)
我们班有十二个学生,都学习中文。两 个中国老师教我们。我们每天有四节课,上 午、下午都有课。我们学习新课文,也复习 旧课文。我们每天念课文,这些课文都不难。
我们的教室不很大,有十二张桌子、十 五把椅子。桌子和椅子都是新的。
(-)
A:你们每天下午都有课吗?
B:我们上午有课,下午、晚上都没课。
A:晚上你们复习不复习?
B:复习。
A:老师晚上辅导你们吗?
B:不,晚上我们自己复习,老师下午辅 导。
A:你们的课文难不难?
B;不难,课文都很容易。
?• 文 中
Lesson 4C (EC、25)
_> 范句 Fànjù Models
? 列 ?• Ú ? ZW ?, , ?个窘 ?志你“文哪铅谁 人杂 > 一中
是U 教的是 国本,?们 哪哪笔谁你师谁报 钢 ,老画 是看 是教 是 枝 个本. 你你哪他谁送这运 • ■ • • • • • 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
什么?
什么.名字?
?•
学-叫'是 你你这 9.,10,11.
(五)
学校怎么样?
怎么样?
怎么样?
志笔 的杂钢 们本枝 你还料 • • • 5 6 7
? ?
?儿会 儿哪宿 哪
在是 在
室儿 他教哪 Z
111

0
二、课文 Kèwén Text
㈠
A:你是哪国人?
B:我是------人。
A:你叫什么名字?
B:(我)叫 ----------
A:你现在学习什么?
B:(我现在)学习中文。
A:你在什么学校?
B:我在------
A:你以后学什么专业?
B:(我以后)学历史。你现在
学什么专业?
A:我现在学化学。
B:你在哪个学校?
A:我 在 ----------
(三)
A:这些书是谁的?
B:这些书是我们的。
A:这是什么书?
B:这是语法书。
A:这本语法书怎么样?
B:这本语法书很好。
A:谁教你们语法?
B:张 老师(教我们语法)。
A:张 老师现在在哪儿?
B:(现在张老师)在她的办公室。
A:张 老师的办公室在不在
这儿?
B:(张老师的办公室)不在这儿, 在那儿。
Lesson 4D (EC 26)
—、词组和范句 Cízù hé fànjù Word Groups and Models
一九一七年
2 - 一九四九年
3 .今天(是)
4 .今天(是)
5 .今年(是)
6 . --•八七--■年
十一月七日(号)
十月 日(号)
几月几号?
星期几?
一九七几年?
三月十八日(号)
课文 Kèwén Text
L 一年有几个月?
一年有十二个月。这十二个月
是:一月、二月、三月、四月、五月、 六月、七月、八月、九月、十月、
H—月、十二月。
2. 一个月有多少天?
(一个 月 有)三十天 或者三十一天。
二月 只 有 二十八天 或者
二十九天。
3. 一年有多少天?
(一年有)三百六十五天或者
三百 六十六天。
4.一个星期有几天? 「 二
•-个星期有七天。这七天是: 星期一、星期二、星期三、星期四、 星期五、星期六、星期日(星期天)。
5.今年是一九七几年?
(今年是)一九七一年C
■ ■ ■ ■ : . : ■■ , 」,
■■ .[ ■■ ■ . -
*去年,,是「一九七O年。
7・明年是一九七二年。
8.上(个)月是几月? 上(个)月是九月。
8这个月是七月J : :
;> -- ■ - -
10 .下(个)月是十一月。
; ■<-
11 .今天一 是 几:号(日)?
(今天是)五号(.日)。
• : , ■
12 .昨天是四号(日)。
⑶明天是九月几号?
(明天是)十月六号。
14 .今天是星期几? (今天是)星期二。
15 .昨天〔是星期一。
⑹明 天是星期三。
Lesson 5
New Words with Old.Characters
a.一起 yìqí N: together (like 一 块儿)
New Characters and WordS
jing京lA* 南龙东
京
*
2•首 shou
BF: capital (of a country)
nánjīng N: Nanking (lit. southern capital)
beijīng N: Peking (lit. northern capital)
dongjīng N: Tokyo (lit. eastern capital)
BF: head; chief, principal
(Note
首都Shoudù
that in this usage
N: capital (of a country)
is pronounced du,)
3.留 liú
留下
留条儿 瑞学 爷学生
liiíxia* liúqilai* liútiáor*
liúxué liuxuéshěng
V: keep or set aside (for later use); detain; leave behind; stay (in a place)
RC: leave (it) here
RC: put (it) away
VO: leave a note or message
V: study abroad
N: overseas students
4.始 shī BF: start, begin
开 夕台 kEish工 V: start, begin

5-机微产
才几会jWhui* 留⑶机 liúshēngjī*
BF: machineí opportunity
N: opportunity
N: phonograph
(飞)机 fēijī*
N: airplane
6.器(器)qi
N: tool, utensil, device
7.袜
8.息
xiū
xi
N: machine, piece of machinery; engine; radio set (M: 广― ,
BF:
BF:
rest; take a break resign
breath; stop, rest
or
你急
xiūxi*
rest, take a break
or
9.参修)cètn
BF:
join, participate,
vacation;
vacation
take part
join, participate,
take part
10.观勰)gu五n
BF:
observe;
view

cānguān*
visit (a
place), tour
11.制(裂)zhW
BF:
fashion, manufacture;
cut out, regulate, fix, limit, control; set of rules, system
12.造 zào
BF:
do, create, make, fashion, build
制造 zhìzào
V:
make, manufacture
中国制造^zh6nggu6 zhìzào
nmade in China”

N: factory, plant, repair shop
N: manufacturing plant, factory
N: factory
Translations of the Usage Examples
2. The capital of China is Peking.
3. I hope to go to China to study.
There are many American students studying in Peking.
4. We start work at 6:30 a.m. and get off at 5:00 p.m.
6. This aircraft Ts engine is on the blink.
13. There are many automobile factories in the northern U.S.
在工厂参观.

语法 Yùfà Grammar
1) The prepositi0nsit从》,《在》,《跟》 always take objects to form prepositional constructions which are often used as adverbial adjuncts.e.g.
我从宿舍来。
我在教室学习。
我跟他一起练习发音。
2) Several verbs or verbal constructions can be used successively as the predicate, e, g.
我去上课。
晚上我们去图书馆看书。
Lesson 5A (EC 27)
一 ■一 ■ ■ ■
一、范旬 Fànjù Models
(一)
1•您从哪儿来?
2.我从办公室来。
3.他从哪儿来?
4.他从宿舍来o
10.我们在教室上课。
11 .我们在图书馆看书、看报。
12 .老师在教室辅导我们。
(三)
13 .他跟我说英文。
5.老师从教室来。
6.我们从学校去。
(二)
7.他们在中国学习。
8.他们在北京学习。
14 .我们跟老师说中文。
15 .我跟他 ■•-起学习o
16 .我跟我的同学一起练习 写汉字。
9.他们
在北京大学学习中文。
二、课文 Kèwén Text
张老师是北京人。今年八月
十五号他从中国的首都北京来° 以前,他在北京大学工作,教外国 .留学生中文。从十月一号开始他
教我们。
中文发音容易,语法 ,也不难。
我们都努力学习。张老师常常在 教室辅导我们,跟我们一起练习 发音,分析句子。我们也常常去 他的休息室问问题。
下星期一我们 不上课,去参观 一个 机器 制造厂。张 老师 也 去。

一起参观北京大学
Lesson 6
New Words with Old Characters
bian(r) qiánbiān(r) hòubiān(r) shàngbiān(r) xiàbiān(r) lībiān(r) wàibiān(r)
边过边过过ii 前后上下里外
BF: (localizing suffix)
N: front, in front, before
N: rear, in back, behind
N: top, on top, above
N: bottom, at the bottom, below
N: inside
N: outside
b.中间 zhongjian(r)
N:
middle,
center, between
c.思登、sīxiang
N:
thought, thinking, ideas, ideology
ze
New Charac t e rs and Wo rds
1.旁 pang
BF:
side,
flank; close at hand
2.
3.
啻也 pángbiān(r)*
du an
炼(爆liàji À).
N:
BF:
BF:
V:
VO:
VO:
side,
forge
smelt
beside, alongside
temper, steel (either lit. or fig.); do physical training
do physical training the body)
(lit. temper
temper oners thought (by reading works of Mao, doing labor, etc.)
temper oners thought
iàn力话报车门Ing影áng d电电电电电y电t
ruaL
shí
|
diànlì |
N: electric power, electricity^ |
|
diànhuà* |
N: telephone, phone call |
|
diànbào* |
N: telegraph, telegram |
|
diànche* |
N: trolley car |
|
diànmén* |
N: electric switch |
|
BF: shade, shadow, reflection | |
|
diànying(r)* |
N: movie, motion picture |
|
BF; hall, spacious room | |
|
litáng* |
N: auditorium |
|
jiàotáng* |
N: church (building) |
shítáng
BF: eat; food
N: dining hall, cafeteria
8.场(以 chSug
(④机场 fēiJíchǎng*
BF: field, arena, stage
N: airport, airfield
9.
cāo
BF: exercise, drill, train
N: athletic field, playground

10. 座 zuò BF• seat
M: (large objects such as buildings, cities and mountains)
儿住山4 座星座
一座 几
11 .楼(脸]
zuòr* N: seat 机
zuòwei* N: seat
yízuò shān a mountain
jlzuo fángzi several houses or buildings
N: multistory building
M: (floor of a storied building)
12.园(Rl) yuan
回孑 yu£nzi*
£ I到 gōngyuán*
13. dian
有店 shūdiàn fàndiàn*
BF: garden
N: garden
N: park (lit. public gardeíis);;
BF: store, shop, inn
N- bookstore
N: hotel, restaurant, inn
shāng
shǎngliang* shāngdiàn
商业 shāngyè
BF: discuss; trade, commerce
N- discuss, talk over
N: store, shop
N: commerce
lóushàng* N: upstairs
|
shànglóu* |
VO: |
go upstairs |
|
lóuxià* |
;N: |
downstairs |
|
xiàlóu* |
VO: |
go downstairs |
|
èrlóu |
N: |
second floor |
|
yízuò lóu |
a building |
15.械尚)sh®
16.社 she
shèhui
旧社会 jiù shèhui
公社 gongshè
N: tree 、
BF: society, community; association, corporation, agency
N: society
N: social life
N: the old (pre-communist) society
N: commune
Translations of the Usage Examples
c. The Chinese people are vigorously studying Mao Ze-dong thought.
7. Our school cafeteria is between the auditorium and the library.
9. Wien class lets out at noon, the teachers and students exercise on the athletic field.
14. They sell bicycles upstairs at The East Is Red store.
16. There are considerable differences between the American and Chinese societies.
There are several people1s communes outside Peking.
语法 Yǔfá Grammar
a上,下,里,外》are generally not used by themselves but adhere to nouns to show locality, e. g. «桌子上口楼下”,《教室 里城外乙
“上边,下边,里边,外边,上头,下头,里头,外头》etc. are nouns of locality. They can be used singly or qualified by other nouns. e・g•“桌子上边》J教室里头》「宿舍外边
〃有》sometimes shows existence and the subject is usually a word or phrase denoting locality, e. g.
书架上有很多书,还有不少杂志。
公园(的)西边有一个人民公社。
我桌子上没有报。

Lesson 6A (EC 28)
一、范句 Fànjù Models
(一)
1 .他在前边。
2 .我在后边。
3 .你在我们(的)旁边。
4 .那张桌子在两把椅子(的)
中间。?
(-)
5 .上边的报是:今天的。
6 .下边的报是昨天的。
7 .这间教室里 的 桌子都是新的。
8 .这个 书架上的
书 都 是中文的。
宿舍楼 食堂
教室楼
学校前边
(三)
,我们的学校在城外。
10 .我们的教室在这座楼里。
11 .教室在楼下,图书馆在楼上。
(四)
12 .教室里 有 很 多 桌子 和
椅子。
13 .图书馋里有很多书、报、杂志
和画报。
二〉课文 Kèwén Text
这是我们的学校。
我们的
学校在城外。学校里有教室,有 图书馆,也有礼堂、宿舍和食堂。 图书馆 在 教室楼里,教室 在 楼下,图书馆在楼上。宿舍楼在 教室楼 后边,操场 在教室楼 前边。
教室楼在宿舍楼和操场的中间。
宿舍楼旁边是食堂。
我们每天都在教堂(里)上课, 在 食堂(里)吃饭,在操场(上)
锻炼,我们 也常常在礼堂(里) 看电影。
Large-scale basic farmland construction in the Plum Blossom Village commune.
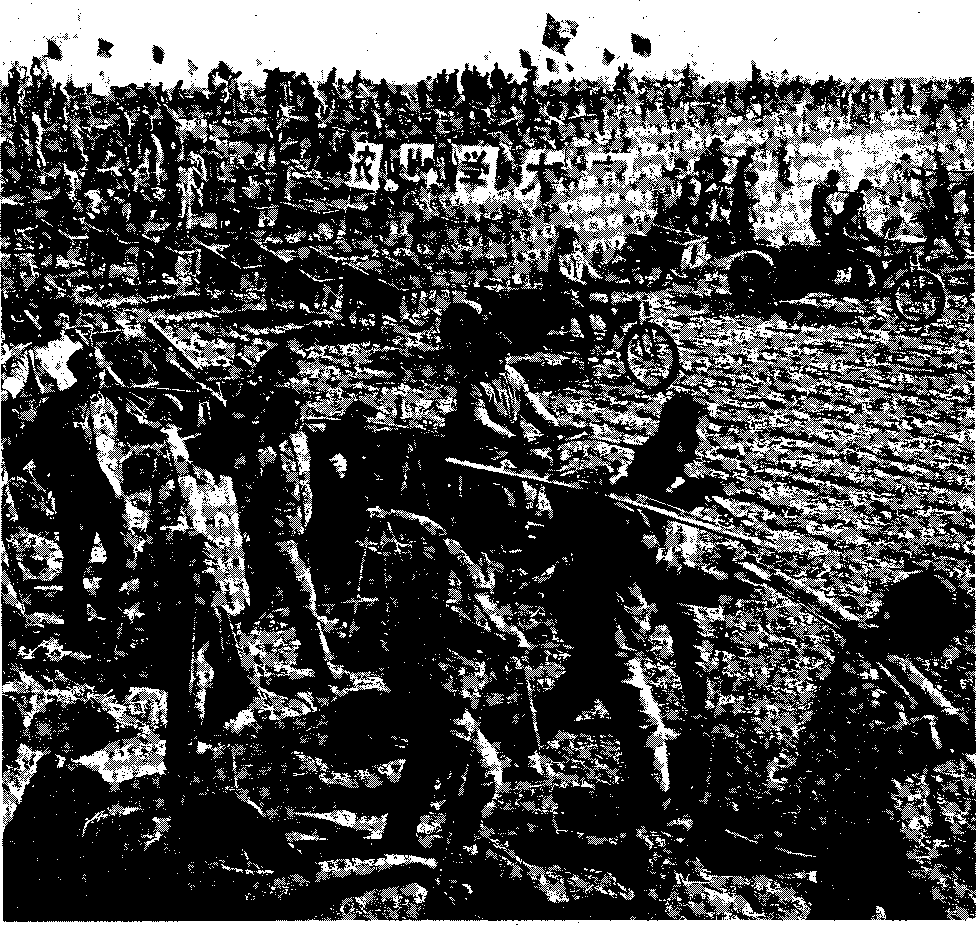
Lesson 6B (EC 29)
一,词组和范句 Cízǔ hé fànjù Word Groups and Models
|
(一) |
(四) |
|
13.商店 |
在什么地方? |
|
L东--东边 |
(二)
8-学校的北边 (三) 8东边的学校 10.西边的工厂 11.南边的公园 ⑵北边的商店 |
W.这条街上有很多商店。
1工厂宿舍大 l 商工厂 固街--- 永瞰缸大,街,…1 |
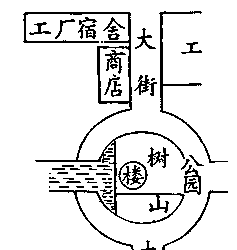
二. 课文 Kèwén Text
这是一条大街。街(的)北边有 一个商店,商店里有很多人,他们在 那儿买东西。这个商店的东边还有 一个很大的书店,书店里的人也不 少,他们都在那儿看 书或者买书。 这条街的南边有一个很大的公园, 公园里有山,有水,也有树。公园的 西边是人民公社。
(二)
北京有很多 学校。他们的学校在 这条街的西边。学校(的)北边有 一个商店.,还有一个食堂。;西边;.是 人民公社。学校(的)南边还有一个 机器制造工厂。
Lesson 6C (EC 30) (Review)
_、词组 Cízǔ Word Groups
(一)
|
学校教室图书馆 |
前边 |
|
山食堂宿舍礼堂 |
后边 |
|
工厂书店商店 |
左边 |
|
我你他 |
右边 |
|
老师 |
旁边 |
(二)
|
学校工厂图书馆 教室办公室宿舍 食堂礼堂公园 商店书店 课文电影 |
里 |
|
书画报杂志本子楼 | |
|
上 | |
|
纸报桌子 椅子操场 |
(三)
|
前后旁里外左右 |
的 |
椅子 桌子 |
|
边边边边 东南西北 |
学校 工厂 公园 商店 |
(四)
|
在 |
中国北京 | |
|
学校教室办公室图书馆 操场宿舍食堂礼堂公园 工厂人民公社书店商店 | ||
|
前边后边上边下边里边外边 左边 右边 东边 西边 南边 北边 | ||
|
你(们)他(们)我(们) |
这儿 | |
|
老师朋友 |
那儿 | |
(五)
|
从 |
教室操场 |
来 去 |
|
那儿 | ||
|
城里城外 | ||
|
他那儿老师那儿 | ||
|
这儿 |
去 |
(六)
|
二 |
两 | |
|
1 |
第二天 |
两天 |
|
2 |
第二年 |
两年 |
|
3 |
二月 |
两个月 |
|
4 |
星期二 |
两个星期 |
|
5 |
第二节课 |
两节课 |
|
6 |
第二课 |
两课 |
|
7 |
第二课课文 |
两课课文 |
二、句子 Jùzi Sentences
(-)
|
1 |
今天是星期几? |
一二三四五六日 |
|
2 |
现在是几月? |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Í1 12 |
|
3 |
今天是几号? |
1 3 8 10 12 20 22 27 28 30 |
|
4 |
今年是一九七几年? |
1970 1971 |
(二)
|
1 2 3 4 |
我, 他 你 她 |
跟 |
他 老师 我同学 我朋友 |
(一起)说中文。 |
(三)
|
谁 |
他是学生吗? 他是不是学生? 他是谁? 谁是你的老师? |
是。 是。 是我的老师。 他是我的老师。 |
|
谁的 |
这是你的书吗? 这是你的书不是? 这是谁的书? 这本书是他的吗? 这本书是不是他的? 这本书是谁的? |
是。 是。 我的书。 是(他的)。 是(他的)。 是他的。 |
|
哪 |
哪本书是他的? |
这本。 |
|
什么 |
这是'一本中文书 吗? 这是不是一本中文. 书? 这是一本什么书? |
曰 O 是。 中文书。 |
|
怎么样 |
这本书好吗? 这本书好不好? 这本书怎么样? |
很好。 很好。 很好。 |
|
什么地 方 哪儿 |
他是不是在北京学 习? 他在什么地方学 习? 她在哪儿学习? |
是。 在北京大学学 习。 在北京大学学 习。 |
|
什么 |
她学中文吗? 她学中文不学? 她学什么? |
子O 学*文。 |
Lesson 7
New W。工ds with. Old Characters
a.
P:
(adverbial 1 deT)
listen attentively
do gladly
eat slowly
b
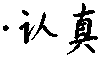
rènzhēn
SV:
conscientious, serious
A: conscientiously, seriously
不象尸做什么,都是认真地较°
c.方次^ fang fa N: method, way, approach
■ ■ V > jiějue
d.1旦是dànshi
A:
but
New Characters and Words
V:
BF:
flow
flow, current
qìliú
shulliú
diànliú
N:
N:
N:
(air) current
(water) current
(electric) current
BF: profit, advantage, gain, benefit
V: utilize, take advantage of, use
|
修清 qīng |
SV: |
clear |
|
k 水很流 | ||
|
8.楚 chú |
BF: |
clear |
|
涛•篁 qīngchu* |
SV: |
clear |
|
9.误(惧)g |
BF: |
mistake |
|
铭诙cubwu |
N: |
mistake (like /L ) |
|
10.握 wò |
BF: |
grasp, hold in the hand |
11. zhang
学 f星 zhangwò
BF: palm of the hand; have in the palm of v one 1s hand
V: take in hand, take charge of, handle, have a grasp on, have mastery of
12 .整 zheng
整咛 zheng sānnián* 三 sānnián zheng* 超C八 5 zheng bādian* 正 u W: or /\ 点、^bādian zheng* [蹩个(电zhěnggè(de)
BF:
whole, complete, intact
a full 3 years, 3 years exactly
8:00 sharp, 8:00 on the dot
BF:
A:
the whole..., a whole... entirely, completely
13 .齐湃)q:
BF: uniform, equal, even, orderly, neatly arranged, lined up
BF: true, real
SV: accurate, correct
15 .记 jì
汨者 jìzhe
V: note (either in writing or mentally): jot down, record; remember
N: reporter (lit. one who records)
|
记得jide* 氾啬支zhe* 彳3位> jìzhù* |
V: remember V: keep in mind, remember | |
|
RC: |
fix in one1s mind, remember well | |
|
16.较 jiao |
BF: |
compare |
|
^匕掇 bìjiào* |
V: |
compare |
|
A: |
comparatively, rather | |
|
17. bèi |
N: |
back |
|
V: |
turn the back to or on; recite | |
|
from memory (since recitation was | ||
|
traditionally done with the back | ||
|
turned to the teacher) | ||
|
节 bèishū* |
VO: |
recite (from a book) from memory |
|
[背着b咨izhe.・・ |
behind someone1 s back] | |
|
18.活 hu6 |
V: |
be alive, live |
|
者 huozhe* - i |
V: |
alive, living |
|
游乐 3 huóbuliáo* |
RC: |
unable to live |
|
流比来 huóguolai* |
RC: |
come to |
|
生抵 shēnghuó* |
V: |
live, make a living |
|
■,: ■ ; ., , ■ ■ ■ ■ ■ |
N: |
livel.ihood, living, life |
|
[为下次hu6xiaqu |
RC: |
go on living, stay alive^j |
3 . shú (shóu)
SV: ripe;, done, cooked; familiar
多件人^ shúrén*
N: acquaintance, casual friend
4 .声(馨)shēng(r)
N: sound, voice, noise
shēngyin* sìsheng* dàshēngde
N:
N: niàn*
sound, voice, noise the four tones read aloud
5 .调 diào
BF: tune, melody
N:
tone (of spoken Chinese)
6 .非 fei
mE玄不可fēi q" Elk爸* 非帝 fēicháng*
BF: not (opposite of 是 );wrong
must go; insist on going
A: unusually, extraordinarily, extremely
Translations of the Usage Examples
b. Whatever she does, she does conscientiously.
c. It takes different approaches to solve different problems.
1. Rivers can't flow uphill.
2. You should take advantage of every opportunity to speak Chinese. "
He speaks fluent Chinese.
5. In' learning Chině'se one must pay attention to tones.
7. The water is very,clear,
11. It took me a long period of study to master Chinese grammar.
12. I ate the whole thing.
The entiré plan is now complete(>
13. She writes very neat Chinese characters.
.. .. , ■■ ■ ■,
14. His pronunciation isn't too accurate.

北京大学师生认真学习。
语法 Yùfà Grammar
1) A verb can take a complement beside an object after it. One of the different kinds of complements is the complement of degree which shows the extent an action reaches, e. g.
他写得好。
你说得对。
他今天来得很早。
This kind of complement is usually made of an adjective, and the structural particle 得 is put before it.
2) The affirmative, negative and interrogative of the verbcomplement construction showing degree are as follows:
|
肯定 |
否 定 |
提 问* |
|
他写得好。 |
他写得不好。 |
他写得好不好? |
|
他说得对。 |
他说得不对。 |
他说得对不对? |
|
他来得很早。 |
他来得不早。 |
他来得早不早? |
Of course one can also use 吗 to make a question, e.g.
他写得好吗? 他写得不好吗?
3) If a complement is added. to a verb-object construction, the verb must be repeateci. e. g.
他写汉字写得很快。
他说中文说得很流利。
4) 4d3” after a qualifier is written into two different characters. After an attributive it is written as 的 and after an adverbial adjunct, as 地.Compare:
休息的地方 大声地念
我们的学校 注意地听
5) In a sentence with a complicated predicate, in order to make the sentence construction more compact or to make the object conspicuous, the object is often put before the verb, or even at the beginning of the sentence. In a sentence with a complement of degree, if the object is transferred to the front, the verb is not repeated. Compare:
他念课文念得很熟。
他课文念得很熟。the object before the verb 课文他念得很熟。"霁混"如刎力g"

Lesson 7A (EC 31)
(一)
一、范句 Fànj 立 Models
L他来得很早。
2.他起得很早。
3.他念 课文念得很熟。
4.他写汉字写得很快。
5•他说中文说得很流利。
(二)
6 .他来得不早。
7 .他起得不早0
8 .他念课文念得不
9 .他写汉字写得不快。
1。•他说中文说得不流利。
㈢
1L他来得早不早?
12.他起得早不早?
13-他念课文念得熟不
熟?
14.他写
汉字写得快不快?
15.他说中文说得 流利 不
流利?
二、课文 Kèwén Text
谢利在北京大学'学习中文。
他非常努力,他学习得很好。 谢利起得很早。每天早上,
他都大声地念课文,他念
课殳"念得很熟。
谢利非常注意语法。老师分析 语法,他很注意,地听,课文的
意思他 都 懂。他 掌握 语法
掌握
问题
得很好,他回答老师的
回答 得也 很 对,语法
错误很少。
谢利每天都作练习,他作 练习也作得很;认真。
汉字 写得很快,也很清楚。
谢利还常常跟同学一起说 中文,他 说 中文 说 得 很 流利。
L我们 整齐。
2 .我们 流利。
3 .我们 正确。
4 .昨天
5 .以前
清楚。
6 .老师 正确。
7 .生词、 得都
8•你说
9.你写
Lesson 7B 范句Fànjù
(一) 写汉字
说中文
作练习
(二) 的课文,
的生词,
的问题,
课文和
很好。
(三) 中文
汉字
(EC 32)
Models
都写
都说
都作
我念得 我都记
我回答
语法,
得很
得很
得很
很熟。
得很
得很
我复习
怎么样?
怎么样?
1。.每天的生词、课文和语法,
你都复习得怎么样?
二、课文 Kèwén Text
A:他学中文学得怎么样?
B:学得很好。他很喜欢中文。 .■■ ■ ■ ■■ ■■■..: ,
A:他的发音怎么样?
B:比较清楚,但是声调不太
,正确。
A:每天的课文,他念得熟
不熟?
B:念得很熟。
A:他的练习作得对不对?
B:作 得不都对,但是错误
比较少。
A:他写汉字写得快不快?
B:写得不快,比较慢,但是 写得很清楚,很整齐。
A:他每天复习得怎么样?
B:他每天
注意学习
都记一得
都背得
A:你们生活
B:我们生活
起得很
不太晚
还常常
都复习,他非常 方法。以前的生词 很清楚。每课课文 很熟。
得怎么样?
得很好。我们早上 早,晚上睡得也
,每天学习、锻炼, 畲电影或者去参观。
Lesson 8
New Words with Old Characters
... . 、■
a.工业 gongyè
N: industry
Att: industrial
b. j'áj shí jiān N: time
c.电影机diàjiy工ngjí N: movie projector
New Characters and Words
1.展 zhán
笈、底^ f āzhan
BF: unfold, unroll, open, expand
;:
V: develop, expand, grow
.N: development, expansion growth
2.览(霓)lan BF: look over, view, browse
晨^电 zhanlan V/N: display, exhibit
展览会 zhanlanhuì N: exhibition
3.圆 yuan SV: round, circular
|
4.该 gāi |
A: should, ought to; it1s time to...; it1s 一一1s turn |
|
为}焚 yinggāi* |
A: should, ought to |
|
孑亥走 J gāi zou le* |
11f s time to go. |
|
j及力隹3 gnshéi le* |
Whose turn is it? |
|
5.春 chūn |
BF: spring ■■■, ■ - .. , ■ ■■ ■■■ |
|
大^ chūntian* |
N: spring ; ■■ ,, ,1 . |
|
6.夏 xià |
BF: summer |
|
百 W xiàtian* 4c入 |
N: summer |
|
7.秋(烯)qiQ |
BF: autumn |
|
新女 qidtian* |
N: autumn |
|
8.冬 dong |
BF: winter |
|
幺》 大_ dongtian* |
N: winter |
|
9・暖(凰nuan |
SV: warm (of weather) |
|
0 彖冰。nuānhuo* |
SV: (pleasantly) warm |
|
(Note that in this usage |
/p is pronounced huo.) |
|
10•热(即r咨 |
SV: hot 二 . [J |
|
4^ 心、rèxīn* |
SV: earnest, ardent, warmhearted, |
|
V、、、 |
enthusiastic, zealous |
|
11「冷 leng |
SV: cold |
|
12. MÍeng |
N:, wind, breeze .; ■ .■: ■- - . ■ ■. |
|
13.®<W>guā |
V: blow (of wind) .. . .■ ,■ ■ . . ■: : |
|
制风 guāfěng* |
VO: wind blows |
|
14.雨 yù 1南 |
xiàyu* |
N: rain 、 VŌ: rain | |
|
15.雪 xuě |
N: |
snow | |
|
xiaxue* |
VO: |
snow | |
|
16.冰 6K)bíng |
N: |
ice | |
|
17.滑 huá |
V: SV: |
slip, slide, glide; skate; ski slippery (either lit. or fig.) | |
|
huáxue |
VO: |
ski (on snow) | |
|
力赍水huáshui VO: water-ski ^懵,水 hu^bing VO: ice-skate 「 泳太清,我站不起枭. | |||
body
on the body, on one1s person]
|
19.体侬尢工 |
BF: |
body |
|
身够""shěnti* |
N: |
body, health |
|
20.阿 ā |
BF: |
(used in transliterating the sound 1ar in foreign languages) |
|
阿里ālī |
N: |
Ali |
Translations of the Usage Examples
a. China can now be considered an industrial country.
b. It * s time-let * s go.
c. The movie was almost finished when the projector broke down.
1. Chinese industry is expanding very rapidly.
2. I hear China is going to have an industrial exhibition in October of this year.
LetT s go see that exhibit this afternoon!
17. The ice is too slippery; I can1t get on my feet.
There are several famous skiers in France.
18. I don't have any money on me.

语法 Yǔfà Grammar .
1) The modal particle«了》put at the end of a sentence shows:
(1) The appearance of a new state of things (or the state of things has existed, but the speaker has not realized it until now), e. g.
下雨 了 〃 did not rain before, 雨大了。 The rain was not heavy before.
雨 小 了 0 The rain was heavy, but has become light now. 不下了。 It was raining, but the rain has stopped now.
(2) An event that happened in the past. e.g.
昨天我去参观了。
他早上告诉我了。
If ifs not one special event but a constant state of things or something that happened many times, a is not used even if it happened in the past. e. g.
以前他常常跟我一起锻炼。 去年我在北京工作。
2) A noun denoting time used as an adverbial adjunct is put at the beginning of the sentence or in front of the word or phrase it qualifies, e. g.
每天上午我们上三节课。
我们每天都八点上课。
Auxiliary verbs 能,可以,会,耍 etc. are often put before verbs to show possibility or will etc.
1) “能、可以" shows:
(1) Capability, e. g.
那个工厂能(可以)制造很多大机器。 我能(可以)说中文。
(2) Consent by circumstances, e. g.
我们今天晚上不学习,能(可以)去看 电影。
(3) Permission or prohibition, e. g.
这里能(可以)抽烟(chōuyān to smoke) o
But the negative and the interrogative of <the three are not
entirely the same:
|
肯定 |
否 定 |
提 |
问 | |
|
力量 |
能,可以 |
不能 |
能不能? |
能吗? 可以吗? |
|
条件 |
能,可以 |
不能. 1 . . ■ ■ ■ . ;1: ■■■■ 一:- |
能不能? |
能吗? 可以吗? |
|
允许, |
能,可以 |
不能,圣可以. |
能不能? 能吗? 可以不可以? 可以吗? | |
2)会 shows:
(1) A skill, e. g.
他会滑冰,我不会b
你会抽烟吗?
(2) Possibility, e. g.
不会下雨,你去吧。
他会来帮助你。
. ' 1 , L'■ ■. . , ■ ■. -■ - - - - . . 1 ■
3)要 shows:
(1) Wish, e. g.
我要去图书馆。
The negative form is usually «不想”.
(2) Necessity, e.g.
念生词要注意声调。
The negative form is usually “不用》(need not) e. g.
你不用记这个生词。
一、词组和范旬 Cízfi hé fànjù Word Groups and Models
㈠
2:00——两点(钟)
2: 05--两点五分
2:10---两点十分
2: 15——两点十五分
两点一刻
2: 30——两点三十分
两点半
2: 45——两点四十五分
两点三刻
差一刻三点
2: 55——两点五十五分
差.五分三点
3:00——三点(钟)
1-现在(是)
(二)
几点(钟)?
工现在(是)两点。
3・现在(是)十一点十分。
(三)
4.我们每天上午八点(钟)开始 上课。
5.我们每天上午十一点三十五分
-- ■ . .. ■ - ,
下课。
6.每天中午我们休息。
7.每天晚上七点< 钟)我们复习 或者预习。 J
㈣
8・几点 了?
外什么时候 了?
10.三点半 了。
1L上课 了。
12 .休息 了。
13 .下雨 了。
14 .星期日下午你们作什么 了?
15 .今天上午我们参观展览会了。

二、课文 Kèwén Text
(一)
今天 是 星期日。上午八点三刻,我 的朋友阿里来看我。他问我:“你 今天作什么?”我说:“上午复习 中文,下午去看电影」他说:“我们 去参观中国工业展览会好不好?” 我说:“我很喜欢看展览。几点 开始?” 他 说:“上午 九点半 开始。” 我说:“好,现在九点 了。我跟你 一起去。”
参观展览的人很多,有不少 中国朋友在那儿工作。九点四十分 我们 开始 参观。阿里 问 我:“那个 电影机上 写的是什么?”我说:“写 的是:电影机,一九七。年,中国制造产 阿里说:“这个电影机很好。”
4—点三十五分我们去休息。休息 以后,我问阿里:“现在差五分十二点 了,还参观吗?”阿里说:“他们中午 休息,我们去吃饭,好不好?” 我说:“好」
(二)
我有一张圆脸,
两只手,一只长,一只短。
人们常常来看我,
我告诉他们时间。



_、范句 Fànjù Models
(一)
1.我们 上午从八点 到十一点
三十五分上课。
2.我们从星期一到星期六都 有课。
3.从一九七一■年 到 一九七二年,
他们学习中文。
4.从一九七二年 到一九七六年
他们学习专业。
J
5.他会说中文。
6.他能看中文报。
7.我要去锻炼。
8.我们应该努力学习。
(三)
9.他会不会说中文?
1。・他能不能看中文报?
二、课文 Kèwén Text
一年里 有 春天、夏天、秋天 和 冬天。
北京从三月到五月是春天, 六月 到 八月「是 夏天,九月 ,到.十一月 是秋天,从十二月 到二月 是冬天。
北京的春天天气比较暖和。从六月 开始是夏天,夏天不 太热,七月 和 八月常常下雨。北京的秋天不冷 也不热,很少刮风,天气很 好。冬天 不 太冷,但是有的 时候 刮风或者下雪。
北京的冬天可以滑冰,不能 滑雪。我不会滑冰,今年冬天 我要学。
我们应该努力学习,也要常常 锻炼身体。
Lesson 9
New Words with Old Characters
a. àiren
N: spouse, wife or husband
b.工人 gōngren
N: worker
c.夕卜 ^T^wàiwén N: foreign language
New Characters and Words
1 .讨 t áo
讨饭 taofan
2 .论篇)liìn
时论 taolùn
不论 búlùn*
V:. seek, ask for, request, demand
VO: beg (as a means of livelihood)
BF: discuss or debate (principles)
V: discuss, debate
N: discussion, debate
A: it doesnT t matter, no matter what
3. fan
监例曝头f式11 g^ntou fānchéng 黜(成)美之 yīngwén*
V: flip over/ turn over; translate
VO: turn a somersault
translate into English
4.译牌)yì
翱诈
fānyì*
BF: translate
V: translate, interpret
N: translator, interpreter; translation
5 •申毓黝 匐 彳什么
彳么
你来这里干什么?
gàn gān
gàn shénme (or) gànmá
V: do, be engaged or involved in
SV: dry
What are you up to?, What are you doing?
6.收(4X)sh6u
收条 shoutiáor* 收音机 shǒuyǐnjǐ
我去年迂生日,爱人送给我一架妆啬机.
receive, accept, collect
N:
N:
receipt
radio (M:颦 or^^jjbù)
7.斤(勉)jin
M:
catty (about 1 1/3 pound)
8.糖
tang
N:
sugar, candy (M: £夬 for piece, 斤 for catty, 包 bho for bag)
9.胞 féi
BF:
fat (of animals); fertile (of land); fertilizer
[下月已xià1f"
今年什么时候下胆?
VO:
fertilize, spread fertilizer [
10•皂(阜)zàx? BF: soap
月匕皂 féizào N: soap (M: 土夫 bar)
在公社商店可以买到肥皂。
H.WM)zhou
年很 闰周 r
zhounián
zhoubào
M: cycle
BF: cycle, period; cyclic, periodic
M: anniversaryJ
N: periodical, weekly-magazine or journal
Peking Review
12.jl3*®)dēng
电灯 diàndēng*
红灯记 hóngdēngjì
N: lamp, lantern, light
N: electric light, tTthe lights”
N: Account (record, tale, etc.) of the Red Lantern
BF: inside, interior
[以内 yínèi
N Suff: within (opposite of
内容 nèiróng
丛夕卜)]
N: content, substance; contents
Translations of the Usage Examples
a. My wife/husband works at the May Fourth Pencil Factory.
b. There are over 100 workers at this bicycle factory.
c. Do they sell foreign language magazines at that bookstore?
2. They are now discussing the problem of commercial development in Nanking.
5. What are you doing here?
6. My wife/husband gave me a radio for my birthday last year.
9. When are we going to fertilize this year?
10. You can buy soap in the commune store.
11. 1976 is the 200th anniversary of the United States.
Peopler s Bookstore has Peking Review in English.
12. There1s no one in that classroom-why are the lights still on?
13. 1111 have dinner ready within ten minutes.
What was covered in that book?

语法 Yufà Grammar
1) The suffix 了 (lé) is added to a verb to show completion of action. Compare:
⑴我买一本中文书。
(2)我买了 一本中文书。
Example (1) means that one wants to buy a book but has not bought yet, while example (2) means that the book is bought already.
2) The negative of 买 is 不买,while the negative of;买了 is 汉(有)买(note that in the negative form, the verb must not take 了). Compare:
(3)我不买。
(4)我没(有)买。 ■1 . '' -
Example (3) means that one is not going to buy or doesn't want to buy, while example (4) tells the simple fact that one did not buy.
3) The interrogative form of a verb showing completion of action corresponding to “买不买》应“买了汉,有(Note: “汉有买” can also be said as “汉买》,but “买了 汉有力 cannot be said as “买 了涩"° "涩》cannot appear at the end of a sentence.)
4) When a personal pronoun is used as an attributive possessive before a term denoting kinship or other relationship, the struc-tund particle 的 is not necéssary. e.g・"他爰人",“我同学抬
Lesson 9A (EC 35)
—1 范旬 Fànjù Models ㈠
L我朋友买了 一本《人民画报》。
2-我们学了 一课新课文。
3.他们讨论了 两个问题6
4•你们下了课干什么?
我们下了课去锻炼。
(二)
5.你作了 练习没有?
没有。
6.你们昨天看了 电影没有? 我们昨天没看。
7.练习里的句子,你们翻译了 吗? 她翻译了,我没(有)翻译。
二、课文 Kèwén Text
㈠
李华和他(的)爱人都是
工人。他们 的 工厂 在 城外。昨天
是星期日,他们一起进城了。
他们 先去 参观了 一个 展览会。
看了 展览会,又去买东西。他们 买了 一架收音机、三斤 糖、两块肥皂 和一点儿别的东西。
(二)
A:昨天(是)星期日,你作了 些 什么?
B:上午我在学校复习了 两课 课文。下午我和一个朋友去 看了 一个电影。 看了 电影, 我们又去买了 一点儿东西。
A:新的《北京周报》你买了没有?
B:没有买,我们没有去外文 书店。

工人们正在认真看书学习
Lesson 9B (EC 36)
一、词组 Cízú Word Gronps
㈠
|
能 |
说(中文) |
|
写(汉字) | |
|
应该 |
(二)
|
从 |
八点(钟) |
到 |
十二点(钟) |
|
星期一 |
星期六 | ||
|
一九六五年 |
一九七一年」 | ||
|
宿舍 |
教室 | ||
|
学校 |
工厂 | ||
|
北京 |
上海(Shanghai) |
二,句子 Jùri Sentences
.
(T
|
现在(是)几点? |
1:00 2:00 5:00 7:00 10:00 12:00 |
|
现在(是)什么时候? |
1:05 2:12 2:15 2:30 245 255 12:10 12:20 430 730 |
(二)
|
1 |
他来得早 吗? 他来得早不 十? |
他来得很 早。 |
他来得不 早。 |
|
2 |
你复习得好 吗? 你复习得好 不好? 你"习得怎 么样? |
我复习得 很好。 |
我复习得 不太好。 |
|
3 |
■) 他诜中文说 得流利吗? 他说中文说 得流利不流 利? |
他说中文 说得很流 利。 |
他说中文 说得不流 利。 |
|
4 |
你母汉字片 得整齐吗? 你写汉字写 得整齐不整 Jr? ....... 你写汉字写 得怎么样? |
我写汉字 写得很整 齐。, |
我写汉字 写得不(太) 一整齐。 |
|
5 |
:他语法掌握 得好吗? 他语法掌握 得好不好? 他语法掌握 得怎么样? |
他语法掌 握得很好。 |
他语法掌 握得不太 好。 |
|
6 |
你们课文念 得熟吗? 你们课文念 得熟不熟? 你们课文念 得怎么样? |
我们课文 啷念得很 熟。 |
我们课文 都念得不 熟。 |
(三)
|
我 |
作 |
了 |
两一 个 |
句子。 |
|
买 |
两本 |
书。 |
(四)
|
1 |
你买了书 吗? 你买了书 没有? |
我买了。 |
我没(有) 买(书工 |
|
2 |
你们去锻炼 了吗? |
我们去锻 炼了。: |
我们没 (有)去锻 炼。 |
|
3 |
你初下了课 去哪儿? 你们下了课 干什么? |
我们下了 课去图书 馆。 我们下了 课去参观。 |
三 i 课文 Kèwén Text
星期六吃晚饭的时候,我坐在谢利的旁 边。他告诉我八点半礼堂有电影,问我去不去 看。我说明天要去看展览,今天的课我还没有 复习呢。谢利说:“这个电影非常好,你应该 看,我们一起去。吃了饭,我来帮助你复习」
吃了饭以后,谢利帮助我复习。我问了他 一些问题,他认真地回答了我的问题。八点 一刻我们两个人就一起去看电影Q这个电影 叫《红灯记》,内容非常好。我们都很喜欢。

New Words with Old Characters
a•同志 t6ngzhi N: comrade
N: workshop, machine shop
C•条件 tiáojiàn
N: conditions 9 terms
N: working conditions
N: living conditions
shuīpíng
N: level, standard (lit. water level) Att: horizontal
N: standard of living
g
n zo í u p hvl g u n h -e s
水
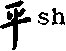
New Characters and Words
1.提 tí
tíchu(lai)
才是周tigāo
V: raise, bring up, remind, propose, suggest
RC: bring up, put forward, suggest | (an opinion, plan, idea, etc.) |
RC: raise (standards)/heighten (consciousness) ;improve or develop
2.实(第sh:
实在^ shízài*
BF: true, real, actual
SV: true, real, actual
A: truly, really, actually
实在地比 shízàide shuo*
to be honest with you, to tell you the truth
3.践谶)jiàn
...■■.. : , :
矣威shíji沔
BF: implement, execute, fulfill
V; put into practice
N: practice
Att: practical
I 公立 ef shèhui N: social practice |
L科玄六两 shíjiàn J
4.动(ÍÙ) dong
dòngbuliao* dòngshēn* huódòng ;:
V:
;«■■■ >■
RC: .; <-
VO:
,N: Att:
move, touch 〜 ī ■
can1t move
start on a journey
activity-
active ,moving, movable
■ , ■ - 1 : ■■ i'.
■■■ ;■
practical activities
social activities
5.况(7兄)kuàng
BF: conditions, ci出umstances, situation
qíngkuàng
N: conditions, circumstances, situation
** 来自 means Tcome from,1 as in (most of them came from Peking).
6.种(槿)zhong
M: kindr type, sort
nàzhong rén*
that kind of person
7. 品 pin BF: goods, commodities, merchandise
品 shípin N: foodstuffs, food products]
8.产(麓 chan
BF: produce
产品 生产
chanpín
shengchan
N: product
V: produce
N: production
9 .解(解)j建
V: untie, loosen, unbutton
BF: explain, resolve; understand
V: settle, resolve, solve
V: ascertain, find out; understand
N: understanding
10.介 jiè BF: go or be between
11.绍 shào BF: connect, continue
介乡百 jièshao* V: introduce
介绍信 jièshaoxìn* N: letter of introduction
Translaticms of the Usage Examples
a. Comrade Mao was unable to recite the text.
b・ How many workers are there in that workshop?
c. The working conditions in our shop are excellent.
d. The level of their English isn1t too high yet.
1. The problems raised by Comrade Wang have to do with working conditions in the factories.
The standard of living of the Chinese people has been greatly enhanced.
3. Correct thought comes from social practice.
4. There are many extracurricular activities at our school.
5. Things are different now.
6. Under these circumstances it1s very easy to learn Chinese characters.
7. The Three Star Market sells Japanese food products.
8. This (kind of) product will go into production next month.
9. In due time you111 come to understand the situation here.
11. This usage of this term hasn't been introduced yet.

车间里的故事会。
语法 Yfifá Grammar
1) The suffix « 了》shows only the completion of an action and so whether in the past or in the future, as long as we want to stress the completion of an action, we can use “了汽 If not, even if it's a past action, no “了" is used. E. g,
明天下了课我们一起去。
你到了北京一定要来找我。
上星期每天下雨。
2) ;A sentence in which a verb with ” 了》takes an object without a numeral cannot be used independently unless the modal particle is added at the end. Compare:
Z〒了课,去书店吧。
我们已经吃了饭了。
Í 今天上了两节课。
这本书莪们已经学了三十七课了。
3) “有白勺" when used as an attributive means a part, e.g.
有的人已经来了,有的人还没有来。
What's to be borne in mind is that when a noun takes ”有 的“,it cannot be used as an object. We can only say ”有的字我 不会写"but not “我不会写有的字汽
If the noun after “有的》has been mentioned in the preceding context, it can be omitted, e.g.
谢利买了不少书,有的是中文的,有的 是英文的。
Nouns of time are usually not used with “有的" with the few exceptions of "时候"etc., e.g.
老师常来我们宿舍辅导,有的时候我 们也去问老师。
“有的人》and "有的时候"can be simplified into “有人"and “有时候》•
Lesson 10A (EC 37)、
_,范句 Fàr® Models
㈠
1.他每天下了课,就去锻炼。
2-我复习了 课文,就作练习。
3-明天你们来 了,我们一起去 参观。
4•星期日我作了练习就进 城。
(二)
5.老师给我们讲课文。
6老师给我们分析语法。
7.谢利给他们介绍学习方法。
8.我朋友给我买了 一本画报。
(三)
9.因为他们很努力,所以学习 得很好。
10.因为他说中文, 说得比较
慢,所以我们都听得很 清楚。
11.因为
他课文掌握得很好,
所以
12.因为
问题回多得很流利。
他们常常练习说中文,
所以中文水平提高得很快。
(四)
13-星期六下午有的班去参观,
有的班去看电影。
14.他们不都会英文:有的(人) 会,有的(人)不会。
15.我们常常去图书馆,有(的) 时候看书,有(的)时候看

二、课文 Kèwén Text
参观机器制造厂
星期五下午是汉语实践活动 的时间。有的步去参观,有的班 去看电影。我们 W参观了 一个 机器制造厂。
到了 那里,工厂的一个同志先 给我们 介绍了 工厂 的 情况。茵为 他说得很慢,很清楚,所以 我们都能懂。
听了 介绍,我们就开始参观了。 这个工厂很大,有很多车间, 每个车间的机器都很新。在 那里我们看了很多种新产品。 参观了 车间,我们又去参观工人 的 宿舍。工人 的 工作 条件 和 生活 条件都比较好。
下星期五我们还要去参观一个 工业展览会。
我们很喜欢参观,因为参观能 了解新中国的情况,还能提高 中文水平。

Lesson 11
New Words with Old Characters for, on behalf of, for the sake of, in order to, with a view to, for the purpose of
a•为 J wèi(le)
A:
b.
%港 jìngcháng A: frequently, often, regularly
c. 发生 fāshēng V: occur, develop, happen
d•在先上 zài X shang 至历史上
社会工的
经(济)上的 _向您
Patt:
zài lìshīshang
shèhuishang de huairén
jīn^jishang de wentí
in terms of X, in X, of X
in history, historically
the bad guys of society, social villains
economic problems, problems in economics
zhengzhi ji
New Characters and Words
1.加 jiā
力口起来 力口上
■■ ; . ■■■■.- 1■ ■ ■ ■
力a在一起
jiāqilai*
jiāshang^
jiā zài yìqī*
V: add, increase
RC: add up
RC: add up, plus
add together
多力口 C加ji/
V: join, participate, take part
2.强(强廉)qi£ng
SV: strong, powerful
加福 jiāqiáng
V: strengthen, intensify, increase, build up
3.谊 yì BF: friendship
友福 youyì N* friendship
4.验(飘勤yà1n
经解 jīngyàn*
有X势般y8『gy*
y8ujīngyàn*
BF: examine, test
N- experience
VO: have X experience, have experience in X
SV: experienced
5.交 jiao
交给 jiāogei* 交给他ji五。gH七五*
交海 jiāolíú
文化妇色wgp厚
jiaoliu
亦/ 6不鼓江星。lid
£//心“力 N jīngyàn
V : hand over, deliver
V • hand over to, turn over to turn (it) over to him
V : flow back and forth, give and take mutually, interchange
N: crosscurrents, mutual give and take, interchange
N: cultural interchange, cultural exchange
VO: exchange experience
6」服 fú
农用良 yifu*
BF: clothes; yield, submit; force into submission, overcome
N: clothes, clothing
7.困(眼)kun
困难 kùnnan
BF: distress, difficulty, quandry
SV: sleepy
SV: difficult, troublesome
N: difficulty, trouble
8.克(剋、 kè BF: adequate, capable; overcome
竟服 kèfú V: overcome, conquer (difficulties)
9.
mutual, one to another likeness, picture, photograph
believe, have faith in
fairly, pretty, comparatively
BF:
N:
xi āng xiàng
本目信 xiāngxln
才目 当 xiā_ngd&ng* A:
10.互 hù
BF: mutual, reciprocal
五槐用互吗富△ [互相帮忙喝瑞ng
A: mutually, reciprocally, one to another
help one another
11.决(决)jué
决定 jugding*
7夫心 juéxín
BF: decide, make up one's mind
V: decide, resolve
y8u juéxīn
V: make up oneT s mind, decide; be determined to...
N: resolve, determination; decision, resolution
be determined to..,, be I resolved to... I

xià juéxīn
VO: make a decision, come to a decision, reach a decision
12.改 g^i
》攵彳事J gáÌdelÌX°* gXibuliXo*
3如M gáihSo(le)* 改土尔3 g区ihu£(1e)* 改衣服y*u*
g^iZheng
V: change, alter, correct
RC: can change, can be altered
RC: can't change, can1t be altered
RC: correct(ed)
RC: change(d) for the worse
VO: alter clothing
V: correct, amend
N: correction, amendment
13.原
BF: origin, original, originally
N:
14.成 chéng
SV: okay, satisfactory
V: accomplish, become, turn into
能不成 chéng buchéng* 镰成汉语"nchgng hìnyú*
okay? will it do?
translate into Chinese
15.绩 jī
BF: merit 9 achievement
成绩 chgngji
N- evidence of achievementi grades, scores, marks, results
Translations of the Usage Examples
a. In order to improve my Chinese proficiency I plan to go to China for foreign study.
b. The teacher regularly còachés us.
c. Without frequent practice, mistakes are likely to happen, (or) If one doesn1t practice regularly, it is likely that mistakes will occur.
da England has historically been a great power, but is no longer.
The new China is politically, economically, and culturally unlike the old society.
2. WeTll have to intensify our Chinese studies.
3. To strengthen Chinese-American friendship we should study Chinese diligently.
5. We often have experience^sharing sessions at our commune.
7. Do you have any trouble understanding spoken English?
8. The Chinese people have already overcome all kinds of difficulties.
9. I don1t believe her.
10. The students in our class often learn from one another.
11. I'm determined to overcome these difficulties.
WeT re determined to master Chinese.
12. If any of the characters I wrote is wrong, please correct it.
「 ■ , '' , '''
13. The teacher analyzed the reason for her (spoken) mistake, and helped her correct it as well.
15. Her grades have been very bad this year, and I don1t know what the reason is.
My grades are very poor; the teacher told me to study hard.
语法 Yfifá Grammar
1)A verb, a verbal construction, or a subject-predicate construction, when used as an attributive, must take the structural particle ”的》,e.g・“参观的人力,“学中文的学生。我们上课的教 室汽
2) The«上》after a noun sometimes has an extended meaning: “会上"means in the course of the meeting, “天上"means in the sky, “学习上》and “语法上》means in respect of studies and in respect of grammar. E.g.
他学习上的困难不手。
我工作上没经验。
3) “又…又…"is used to connect a pair of verbal constructions or adjectival constructions to stress the coexistence of both events or qualities. For example:
这一课又有汉字练习,又有翻译练习。 他念课文念得又流利又正确。
Note: 0又“is an adverb and cannot be placed immediately in front of a noun.
一、词组和范句 Cizìí hé fànjù Word Groups and Models
(一)
1 .参观的人
2 .休息的地方
3 .昨天来的学生
4 .从首都来的学生
5 .来得早的人
6 .教中文的老师
7 .学中文的学生
&我们上课的教室
(二)
9.休息的时候 10.学习的时候
1L上课的时候
12•我作练习的时候
相互学习,提高水平。

(三)
13 .为了 加强中 两国人民的
友谊,我要帮助你们学好 中文。
14 .为了 提高中文水平,我们班 的同学常常交流学习经验。
15 .为了 帮助我们克服学习上的 困难,老师经常 了解我们的 学习情况。
(四)
16 .大家在会上已经讨论了 这个 问题。
0•这种句子怎么样分析,书上 讲得很清楚。
18.老师常常问我们学习上有 什么困难。
19:在工作上,我们 互相 学习, 互相帮助,经常交流经验。
㈤
2。.他又是我的老师,又是 我的朋友。
2L这个同志又会中文,又会 荚文。
22他写汉字写得又快又 整齐。
二、澡文 Kèwén Text
我们的学习生活
我们都是新来的学生,今年 九月我们开始了,新的学习生活。
我们学的专业是中文,为了
;二
加强—中两国人民的友谊,我们 学好中文的决心都很大。
」::, ■■■: V ;;」:*
■ .!• ■-: , ■■ ■ '.
教我们中文的老师是中国 人。他为了 帮叨我们克服学习上 的困难,经常 了解我们的学习 情况。上课的时候,老师约同学们 很多练习的机会。他还「常常 问我们问题。我们回答的时候
,. ■■■ .. ■ ■ ■;1
有错误,老师就给T们改丐。他 有时候还嬴大家一起分析发生 错误 的 原因。我们 都 喜欢 这种 上
■<
二
课的方法。
我们班史文的学习成绩很 好。开始的时候,他学得不太 好,但是他不怕困难,有不懂 的地方,就问老师或者别的同学, 所以他提高得很快。现在他 的发音又清楚又正确。我们都 应该学习史文学中文的讨经验。

参加厂里的工人学习班
New Words with Old Characters
a. of kSnéng SV* possible, likely
i A: possibly, likely to
她说她的专业是意大到历史,我想这个不可能e zuìhòu N: final, last, ultimate
工b.取后
MA: finally, at last, ultimately 周同志最后一句冶是“人民万外” 最后他还是去3.
N • in the immediate past or future-recent, most recent, latest; imminent
暴迎自4 zuljln de U 给来 Jiānglái
zuìjin (de)
/ 期 yiqǐ
MA: recently, lately; imminently in the very near future
latest issue, current issue (of a periodical)
New Characters and Words
1.概 gài
大概限算*
BF: general, overall, on the whole
A: in general terms, approximately, probably
V: lend, borrow borrow from X lend to X -;. --
VO: borrow or lend things
3.典 diXn
BF: classic model, canon, code
zìdiM,n*
洞典c£diS,n
汉荚词典h才n-yMg cídiS.n 荚汉词典 yīng-hàn cídiSn
N: dictionary (of single characters and their meanings)
■■ ... .. -. ■. ■ 一. ■. ■ ; "
N: dictionary (of characters and character combinations-words, phrases, expressions, etc.)
N- Chinese-English dictionary
..■■■ , -. ■ ■ ■■■■■ - - - -■ ,,,
N: English-Chinese dictionary
4 .查(查)chá
杳1 字典 chá zìdián*
V: investigate, check, examine, inspect; look up (in a dictionary)
.... ... . 一 :
VO: look up (a word or character) in the dictionary
5 .虽(雎、suì:
.维)虽然* suǐrán*
BF: although
■ ,p . - . ■ ■ ■
、 -1 ■. , '■■■ - ■ ■ ■ ■■
MA: although, even though
6.遍照)biNn
M: time
一通 yibiàn
Nu-M- once
shuo yíbiàn
say it again, repeat once
7.特 tè
BF: special, peculiar
特别&big*
SV: special, distinctive, peculiar A: especially, particularly
8.
BF: necessary
AV: must, Have to, it1s necessary to
Translations of the Usage Examples a, I didn* t understand a word he said-possibly it was Japanese.
ItTs likely to snow today. (or) There1s a good possibility of snow today. *
She said her major is Italian history, but I don11 think it1s possible.
b。Comrade Zhou1s final words were, "Long live the peopleJn
He went after all. (or) He finally did go.
c. Recently he has been in good health.
The contents of the current issue of PeopleT s Pictorial are very interesting.
1. Before analyzing the sentences, the teacher first explained their general meaning to us,
4. I still don11 understand the usage of this word-guess 1111 have to go to the library and check the dictionary (look it Up).
6. He had to repeat (it) quite a few times before I understood, (or) I didn1t understand until he had repeated it many times.
8. If you want to learn Chinese, youT11 have to study the vocabulary and text conscientiously. (or) To learn Chinese itTs necessary to...
语法 Yfifi Grammar
1) The complement that tells the result of an action is called a complement of result, for example in “写清楚"J 写力 is an action, while"清楚"is the result of the action. The same action may come to different results. E.g. “写完》「写清楚》「写整齐》.
The same result may be obtained through different actions. Eg。写完一看完》「作完乙
A complement of result is put immediately after a verb without “得It is usually made of a verb or an adjective.
2) A verb followed by a complement of result has the same usage as that of a verb. It can take an object as well as the suffix “了2 The negative is shown by “汉有”.E.g.
你看完了那本杂志没有?
没(有)看完。
3) The modal particle《吧》used at the end of a sentence gives it a consulting or agreeing tone. E.g.
我们去图书馆吧。
好吧。
1) “看听“tell only the simple actions of looking and listening. When“见"is added as a complement, it indicates that something has been seen or heard. Compare:
我看了,但是没看见。
他听音乐。
我听见外边下雨了。
2) Both the adverbs «又》and «再》indicate repetition or continuation of an action or a state of affairs. The difference is that "又"applies to the past, and “再"to the future. Compare:
老师叫我再念一■遍,我就又念了 一遍 他昨天来了,今天又来了,他说明天还
要再来O
When we want to tell of an action or a state of affairs which did not repeat or continue in the past, we use 再 only. Compare:
他昨天没来,今天又没来。
(“汉来"is repeated.)
他上星期来了,以后没有再来C
(“来” is not repeated.)
Note, a汉再来》can also be said as,再汉来“,but “又汉来》 cannot be said as “涩又来汽
«又力 sometimes can also be applied to the future, but it mostly comes before the verbs or auxiliary verbs "是”「耍”,"该”「可以” etc., and there is the modal particle” 了"at the end of the sentence. E.g. ■
. 明天又是星期三了。
天气暖和了,我们又可以在外边学习 了。
3) The adverbs «就》and 口 才力 have exactly contrary meanings. “就" means that the speaker thinks a number is small, the time is early or a thing is to happen very soon, etc., while“才"means just the opposite. Compare:
这课课文我看了两遍就看懂了,那裸 课文我看了三遍才看懂。
他七点钟就来了。
他七点钟才来。
一、范句 Fànjù Models
(一)
1 .这本画报他看完 了。
2 .那个问题我回答对 了。
3 .老师说的中文,我们都能 听懂。
4我们一定要
(二)
5 .这本画报他
6 .那个问题我
7 .中文报我们 看懂。
(三)
学好中文。
没(有)看完。
法(有)回答对。
现在还不能
8•他看完了 这本画报没有?
9 .那个问题你回答对了 没有?
10-中文报你们现在能不能 看懂?
(四)
11•昨天的学习经验交流会对 我们有很大的帮助。
12 .史文的学习经验对我们的 帮助很大。
13 .我朋友 对 我 说:“我们 一定要克服学习上的困难」
(五)
14虽,然我们学习的时间很 短,但是已经学了不少东西 了
J O
15 .这课课文艮然很长,但是 不太难o '
16•虽然我们说中文说得比较 流利,但是有时候 还 有 一些语法错误。

二、课文 Kèwén Text
在图书馆
上星期我从图书馆借了 一本 中文画报,已经看完 了。今天我 去图书馆还画报。
到了 图书馆,我对那儿的工作 同志说:“同志,我要还这本 画报,我看完 了」
他问我:“都看懂了 没有?”
“有的地方没看懂,但是大概 的意思都懂 了」
“好,给我吧」他放好画报 又问我:“还借别的书吗?”
“我想借一本我 ,能看懂的 中文书,你给我找一本吧」
那个同志找了 一本给我。
我说:“这本书难不难?”
“虽然这本书可能有一些你 不认识的字,但是上边有画儿, 可以帮助你看懂意思。不认识 的字可以查字典」
因为他说得很快,我没 听清楚,又问他:“不认识的字 怎么办?”
“查字典。你有字典吗?”
我说:“没有,我想去买 一本。”

互相交流经验
_* 范句 Pànjù Models
(-)
1•我听见他在楼上大声地 念课文。
2-你看见阿里 了 没有? (我)没有(看见他)。
(我)没(有)看见(他*
(二)
3•你要是去书店,就给我买 一本语法。
4•今天晚上要是有时间,我 就去找你。
5•明天要是下雨,我们就不 去To
(三)
6-我说:“这个问题我没听清楚, 你再给我讲一遍吧。” 他就又讲了 一遍。
7.那个电影很好,我想再看 一遍。
8.他又看了 一遍那个电影。
(四)
9•昨天的课文,我念了 就念熟 了。
五遍
五遍
1。•昨天的课文,我念了
才念熟。 -W ,,:
11那十个生词,他复习了 三遍 就记住 了。
12.那十个生词,他复习了 三遍 才记住。
二、课文 Kèwén Text
辅导
今天下午我去教室的时候, 看见阿里在前边走,就叫他: “阿里,阿里!”但是他没听见。我 又大声地叫,他才听见。他说, 他也要去教室。
三点钟老师来 了,他问我: “今天讲的课你都听懂 了 吗?"我说:“课文懂 了,语法没
听清楚,老师再讲一遍吧。”老师 又讲了 一遍,我才懂了。讲完 了,老师问我问题。有的问题我 回答错 了,老师说:"课文,你念得 不太熟,还要再练习」
我问老师:“为什么学的汉字 我不能都记住?”老师说:“记 汉字要多练习,特别难的一定 要多写几遍。要是写得太少, 就容易忘。”最后老师说:“要想 学好 中文,必须 自己 努力;还 应该 注意学习方法,互相交流经验」
Lesson 13
New Words with Old Characters if only, provided that, so long as
.只要 zhlyao MA:
六要没有 zhlyào méiyou...
barring..., so long as there
are no...
qiè
New Characters and Words
工•遇 yu
遇见加ian
BF: meet with
RC: encounter, happen upon, run into, meet (by accident)
2.谈
tan
谈诂 tánhuà*
V: talk about, discuss
VO: talk, converse
3.照 zhào
煦相 zhàoxiàng*
?《洋目巾才oxi_ 2ng j W *
V: cast light upon: shine on, illuminate; reflect light• look at one1s image (as reflected in a mirror), make an image of (on film)
VO- take a picture, have one1s picture taken
N: camera (M: or bù)
(Note: the character 木目 in this usage is pronounced and means likeness, picture, photograph.1)
4.片 piàn(r) or piān(r)
N: (thin flat item:) card, film, record, tablet (of medicine)
M: slice (of meat, bread, etc.), tablet (of medicine), expanse (of forest, ocean, etc.)
中片片片 照栩唱-
zhaopiàn(r) xiangpian(r chàngpiàn(r)*
yípiàn(r
N: photograph
N: photograph
N: (phonograph) record
Nu-M: one slice of..., one...tablet, an expanse of.••
(Note: while either tone is acceptable tone is generally preferred.)
for片 9 the fourth
láodòng láodongjìé láodònglì.
láodòng rénmín
BF: labor; hard working
V/N* labor, work
N: Labor Day
N: labor force
N: working people, the laboring people
力文彳* láodòng tiáojiàn N: working conditions
6.勤.qin
勒方qínl£。
BF: industrious, diligent, hard working
N: diligence, hard work
SV: diligent 9 hardworking, industrious
8 .单谭)dan
BF: single, singular; odd (number); list; bed sheet
dānshù dānxíngdao jiXndān* dānzi* kāi dānzi* càidān(zi)^
N: odd numbers (1, 3, 5, 7, etc.)
N: one-way street
SV: simple
N: list; bed sheet
VO- make a list
N: menu
N: bed sheet
9.反 fS_n
ki f苴nzh爸ng* 怠对 f^nduì
VJ turn over, reverse; turn against, rebel; be against, oppose, resist
MAi anyway, in any case, in any event
V: be against, be opposed to; go against, oppose; object to
10.侵 qīn
L1.略曙)1M,
彳星用各qlnl催
■ ■ . . ■■■■■ ■■■■■■ ■ ■ :
[修哈者 qīnlUèzhě
日本是哪
BF* invade, encroach, trespass
BF •:, seizě, t ake by force
V: invade, aggress upon
N: invasion, aggression
N: invader, aggressor I
12.故

gùshi*
BF accidental; old; purposeful
N:
story-
13 .兴(真)xìng
.BF::
interest, pleasure, excitement

gāoxing*
SV:
happy, glad A: happily, gladly
14. ® gXn
w8 gSn shuō*
不散■当 bùgKndáng*
A: dare, venture, be so bold as to
I dare say
I'm flattered; you1re too kind
15.勇
y3ng
BF: brave 9 courageous
索散ybngg知
SV: brave, courageous, bold
16.希 XÍ
BF: hope
17.望 wàng
望缨望 甫
一 、?
xíwang*
y3u xīwang méiyou xiwang
BF: look into the distance, look towards, look forward to
V/N: hope
hopeful
hopeless
Translations of the Usage Examples a. If only Comrade Bai would come, we could start the discussion.
So long as you work hard, you1re sure to overcome all difficulties.
Barring foul weather, we shouldn1t have any problem with production.
1. I recently ran into Comrade Wang.
5. Our school is going to the August First (Army Day) Commune next week to temper ourselves through manual labor.
6. That comrade is really industrious.
7. If you hadn't brought this up, it simply wouldn't have occurred to me.
9. Whether or not you object, you still have to do it.
11e What year was the Japanese invasion of China? (or) What year did Japan invade China?
15. He may be very brave, but he's afraid of getting shots.


语法 Yùfá Grammar
1) The verb “至when used as the complement of result indicates direction. E.g.
他们从上海回到了北京。
老师讲到第四十课。
昨天我们还谈到学习问题。
Sometimes it indicates that an aim is attained or an action . ■ .. ■ ■ ■■ ■ ■■ ■ : ; . ■■ ■ ■ ,
has come to a result. E.g.
我在字典上查到那个汉字了。
你买到那本书没有?
2) The verb "在"when used as the complement of result must be followed by a word or phrase of locality. E.g.
我家住在北京。
他坐在椅子 上o (We cannot say “坐在椅子”.) 那本书我放在他那儿了。
(We cannot say “放在他了》.)
3) Some verbs may be reduplicated, and the reduplicated part is pronounced in the neutral tone. When a disyllabic verb is reduplicated, the 2nd. syllable is also pronounced in the neutral tone. E.g. “看看k祝k互记,“想想x道ngx道ng”,“写骂xi权诺”,“讨论 讨论 馅O曲口修ol屯《介绍介绍jièsháojiěsháo^.
The reduplication of a verb. has several meanings:
(1) The action lasts only for a while. E.g.
我们到外边走走。
我想想再告诉你。
(2) The action is Repeated over and again. E.g.
这些句子不太容易,我要多复习复习。
(3) Trial. E.g.
我说说,你看对不对。
Note: (1) When a monosyllabic verb is reduplicated, be inserted in between, but not with a disyllabic verb. E.g.
星期日我要去看一看我的中国朋友。
(2) The suffix a 了力 must be put in between the reduplication. E.g.
昨天我跟老师谈了谈我们的学习问题。
Such case is very rare with a disyllabic verb.
(3) If the verb takes an object, only the verb is reduplicated. E.g. “讲讲故事》「看了看报》「复习复习课文V
Lesson 13A (EC 41)
_、范句 Fànjù Models
㈠
1•上星期日 晚上八点钟他 才 回到学校。
2 .今天我们已经学到第四十一课 了。
3 .每天 晚上 我 都 学习到 十点半。
(二)
%上课的时候,他坐在我 前边。
5 .那本字典莪放在桌子上了。
6.这 些 句子 我 都 写在
本子上了。
(三)
7•你一定能回答这个问题, (你)再想想。
8・今天的课文比较唯,我要 多复习复习。
|
9・史文有 应该给 1也那课语法 又给我 |
很多 学习 经验, 大家介绍介绍。 我没听懂,老师 讲了讲。 146 |
二、课文 Kèwén Text
在张老师家
星期日晚上,我遇见了张老师。
他说;“去我家玩儿玩儿吧」我 就去了。
走到他家,张老师请我 坐下。对我说:“我们练习 用 中文谈话,好不好?”
我说:“好
桌子上有一本中国画报,我 看了看,里边有一些人民公社 的照片。我就请张老师给 我讲讲人民公社。他坐在我
旁边 说,他 公社里,他给 情况,还谈到
家 就 在一个 我介绍了 那里的 中国学生常常到
人民公社去参加 劳动。他讲得 很慢,很清楚,我都听懂 了。
张老师也问了 一些我国的 情况。我给他简单地介绍了 一点儿我国的历史,还讲了 一个 我国人民反对外国侵略的故事。 张老师听了 很高兴,说:“你们 的人民是勤劳勇敢的人民, 我们 两国 人民 要 互相 学习, 互相帮助」
我们又谈了谈学习问题。张 老师告诉我:“中文不难,只要 努力学习,不怕困难,多练习, 多实践,就能学好」
我说:“我一定妾克服困难, 学好中文。”
我们 谈到 九点半。我 走 的 时候,张老师说:“希望你比后 常常来玩儿」

一九五八年六月,周恩来同志在北京,参加劳动。
Lesson 14
New Words with Old Characters
VO: shake hands
V: apply
N: application
A- applied; practical
女用化学 yìngyòng huàxué N: applied chemistry
>iryingyòng fāngfS N: practical application, ~ " practical method
c.热十青r爸qing
SV: warm,: ardent, enthusiastic N* warmth, ardor, enthusiasm 闱同志也淡同志热情的握3握生
VO: run a school
New Characters and Words
1.结 Jié
BF: tie a knot, connect, unite; make a bond or contract; a
bond or knot
hé
结合徒hé
乡吉皤)"ghiin*
V: combine, bring together, join
V: combine, unite, marry
VO: marry
3.待
dài
V: treat
BF: serve, wait upon; treatment
zhāo
V: wave, beckon; recruit; attract
V: entertain, be hospitable to, take care of
N: service, hospitality
才驸会 zhāodàihul
N: reception
raise
耒年行 起举第
jìíqilai*
júshJSu*
jiíxíng
RC:
VO:
raise, lift
raise one's
up
hand
take place (a
hold, have, meeting, ceremony, etc.)
6.让(^) rang
V: yield, give in; let, allow; have (someone do something) CV: by
7.使 shi
BF: foreign emissary
大^更dashl
N- ambassador
大便£窜 dashlgu^n
N: embassy
8.感 gNn
gSnxiXng
BF: be moved or touched, feel; feeling, emotion, sensation
N: thoughts, feelings, reactions (to an event)
BF: meet, welcome, receive
V: welcome
BF: large room, hall
N: living room, parlor
N: dining room
N: mother
N: old lady
12 .军 jūn
N: army; military force
[军 ^jūnrén
N: military personnel, serviceman
13 .海 hai
N: sea
上 ^,shangh3.i N: Shanghai
[您资ijūn N: navy; sailor
14 .色 sè
BF: color
N: color
N: Red Detachment of Women
放j'红色娘孑军"那个电影.
15 .彩 cǎi
BF: multicolored, colored; colors
一也无色彩 dìfang sècSi 豺色c宜s咨
N:
N:
N:
Att:
多自电影diànyìng N: color (literal or figurative)
local color
color
color, in color, colored
color movie
BF:
music
17.舞
18.蹈
音乐东
ymyue
yínyuejiā
N:
N:
wìí
music
musician
N:
BF:
BF:
concert
dance
trample, stamp, tap
N:
dance, dancing
Translations of the Usage Examples
a. After shaking hands, the
two struck up a conversation.
Yqu ought to go over and shake hands with Comrade Qian.
b. The things one learns in school should be applied in onefs work.
, ■ .. ■, ■■ ■, ‘
c. Comrade Zhou and Comrade Tan shook hands warmly.
. : : 「「 . • ・一 • •
d. They teach applied chemistry at the factory-run school. (or) The school run by the factory teaches applied chemistry.

2. Study must be combined with labor production.
3. They treated me very well,.
4e There will be a reception tomorrow evening to entertain foreign visitors.
5. I hear Comrade Zhang will hold a press conference this evening.
7. Ambassador Huang gave a reception for (the) French exchange students.
8. What did you think of the movie?
9. At the reception, Ambassador Rong shook hands with each comrade to welcome them.
10. We're showing a movie at 2:00 in the screening room to entertain the comrades from Red Star Commune.
11. That old lady treated me very well.
12. 11ve come to feel military life isn11 so bad after all.
13. Those three servicemen are probably sailors from Shanghai.
14. Not long ago, DLI showed the movie "Red Detachment of Women.n
15. "Red Detachment of Women” is a color (technicolor) movie. ■ ■ ■- ■1,'「 ,]一 .;■" ■
16. Every day when I get home from work/school, I turn on the radio and listen to music.
18. The culture of northwestern China is different from elsewhere; the music and dances are very distinctive.
语法 Ytìfà Grammar
1) The verbs “来“ or “去“is often used after another verb as a complement which shows the direction of the action of the verb and is called the simple directional complement. If the action is toward the direction of the speaker (or the person or thing concerned) “来" is used, and,去“ is used if the opposite is the case. E.g.
张老师进去了。(说话人在外边)
张老!/币进来了。(说话人在里边)
The object of a verb with a directional complement is generally put between the verb and the complement. E.g.
他上楼来了。
同学们回宿舍去了。
他从中国带了 一架收音机来。
你去拿一把椅子来吧。
Two points must be borne in mind:
(1) If the action is completed and the object is a thing or person whose position is changed by the action, it can also be placed after the complement. E.g.
他从中国带来了一架收音机。
(2) If the object is a noun indicating locality, it can never be placed after the complement. We cannot say「他上来楼了》「同学 们回去宿舍了汽
2) There is a kind of sentence with a verbal predicate which consists of two subject-predicate constructions. The object in the first S-P construction is at the same time the subject of the second one. This is called the pivotal sentence. E.g.
他叫我给他借一本书。
、词组 Cízfi Word Groups
㈠
|
完 |
到 |
好 |
对 |
错 |
会 |
清楚 |
见 |
懂 | |
|
看 |
V |
V |
V |
V |
V |
V | |||
|
听 |
V |
V |
V |
V |
V |
V | |||
|
念 |
V |
V |
V |
V |
V |
V |
V |
X | |
|
写 |
V |
V |
V |
V |
V |
V |
V |
X |
X |
|
学 |
V |
V |
V |
V |
X |
X | |||
|
说 |
V |
V |
V |
V |
X |
V |
X |
X | |
|
用 |
V |
V |
,:V |
【V |
X |
X |
X |
X | |
|
作 |
V |
V |
V : |
V |
V |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|
买 |
V |
V |
X |
X |
X |
X | |||
|
回答 |
V |
V |
V |
V |
X |
V |
X |
X | |
|
练习 |
V |
V |
X |
X |
X | ||||
|
翻译 |
V |
V |
V |
V |
V |
X |
X |
X | |
|
分析 |
V |
V |
V |
V |
X |
V |
X |
X |
Note: aV》shows that the verb on the left can take the complement of result above, and very often does so. shows that it cannot. A blank shows that it can, but does not often do so.
(二)
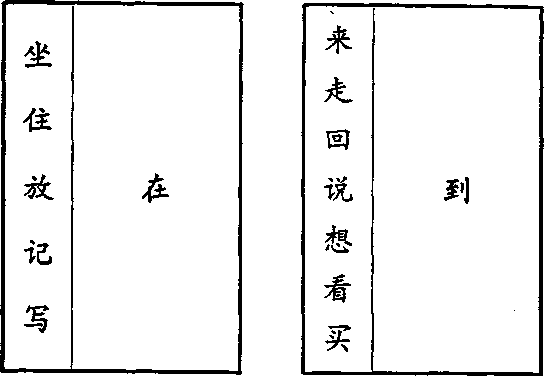
工句子 Jùzi Sentences
(-)
|
我 |
复习 |
了 |
课文 |
(就) |
作 |
练习。 |
|
下 |
课 |
去 |
操场。 | |||
|
买 |
东西 |
回 |
学校。 |
(二)
L我们都是学中文的学生。
2.他是教我们中文的老师。
3•这是我们上课的教室。
4老师给我们讲的语法,我们都听懂了。
5•昨天学的生词有十六个。
6-他们写的汉字很清楚,也很整齐。
7.他说的那个电影,我们都很喜欢看。
&那个同志给参观的人介绍了工厂的情 况。
9.我想看看从图书馆借的那些中文书。
10.现在我们说中文的时候,还常常有发 音或者语法上的错误。
(三)
11.那本书我看完了,但是还想再看一遍。
12.这个字我又写错了,我还要再练习练 习。
13.请你再说一遍,我还没听清楚。
㈣
14.他去年就去中国了。
15.星期日晚上我们六点半就到学校了, 他们八点才到。
16.这几个汉字我写了两遍就会了。
17.那些生词我念了很多遍才记住。
18.这个问题老师又讲了一遍,我才听懂。
三、课文 Kèwén Text
工厂里的学校
这个机器制造厂办了 一个学校。很多工人 在这儿学习。学校里有的老师就是这个工厂 有多年实践经验的工人。
学生上午学习,下午回车间工作。上课的 时候,老师认真教,学生努力学。学生有了问 题,老师就跟大家一起讨论,所以老师教的东 西,学生都能很快地掌握,老师也从学生那儿 学到了不少东西。
因为学生每天都在车间劳动,所以学的东 西很快就能在工作上应用。正因为学的东西 能跟实践结合,所以他们也就掌握得更好。
这个学校的学生很注意互相学习,互相帮 助,经常交流学习经验,所以都提高得很快。
一、词组和范句 Cíztì hé fànjù Word Groups and Models
(一)
L进来 进去
2•出来 出去
3 .上来 上去
4 ・下来 下去
5 .回来 回去
6 .拿来 拿去
7 .带来 带去
8♦到北京来
(二)
10.他已经回去 了。
1L请大家都
12 .下了 课他
13 .史文星期二
进来吧。
回家去了。
到中国去 了。
14 .他们都进教室去 了。
15 .同学们都上楼来 了吗?
16 .我要去宿舍拿一枝钢笔 来。
17 .你去看他的时候带两本 画报去。
18 .他昨天拿了很多照片来。
19 .她去上课的时候,带字典 去了吗?
2 。.他昨天拿来了 很多照片。
21 .她去上课的时候带去了
一本字典。
22 .你的中文杂志他拿去了。
23 .字典谁借去 了?
(三)
24这样的电影招待会我很喜欢 参加。
25 .请你给我一本这样的画报。
26 .这个汉字不应该那样写, 应该这样写。
27 .我要去图书馆借一本那样 的「字典b
㈣
28 .我请一他 ,跟我,一起去参观 中国工业展览会。
29 .阿里 叫 我 给他 介绍介绍 那个电影。
30 .老师让我告诉大家,晚上 预习第四十三课。
二、课文 Kèwén Text
参加电影招待会
上星期六晚上,我和两个朋友 到中国大使馆去参加电影招待会。 我是第一次参加这样的招待会。
招待会八点半开始。那天天气很 好。吃了 晚饭,我们就去中国 大使馆了。我们一边走;一边谈 话。一个从中国 回来的朋友, 谈到了 一些他看 中国 电影的 感想。八点二十,我们到了大使馆。
大使馆的同志看见我们进来 了,就来欢迎我们,跟我们握 手。一个同志带我们上楼去。 走进电影厅,里边 已经有不少 人了。他让我们坐下,热情招待 我们。一会儿电影就开始了。
我们看的电影叫《红色娘子军〉〉。 故事很有意思。音乐、舞蹈、色彩 我都很喜欢。看完电影离开 大使馆的时候,我们对中国同志 说萧谢他们。他们说欢迎我们 下次再来。
从大使馆出来,我们一边走一边 谈看了 电影的感想,都说希望 以后还能有这样的机会。

在公社办的劳动大学学习。

把学习和生产结合起来。
New Words with Old Characters
a.乃争唱gè>ngh3gu6 N: republic
New Characters and Words
1 .华(莘)huá
BF:
多t华字典 xWnhu€ zìdiǎn 中华人民 zhonghuá rénmín 改彳。网 gSnghéguó brilliant, splendid, glorious; China, Chinese
the New China Dictionary
the People1s Republic of China
2.汽 qì
BF: steam
洗军qlchē*
公关汽车 gonggòng qìchē* N:
N:
car, bus
automobile
3 •辆(ÍS) liang
M: vehicle
4 . lie BF: line up one after the other
M: train
5 .代 dài BF: substitute for, take the place
of, act on behalf of
4十 段 d^ibiǎo V: represent, speak for, stand for
N: representative, delegate
6 .团(虱,橱)tuán N: group, regiment, corps
仿的团 lìíxíngtuán* N: travel club, tour group
代表团 dàibiǎotuán N: delegation
7.
kē
nèikē*
waike*
kěxué
kēxué fǎngfa kěxuéjiā zìrán kēxué shèhuì kexué
yìngyòng kēxué
BF:
N:
N:
N:
N:
N:
N:
N:
N:
class or categoryí field (of study); branch (of medicine);
family (of plants orí animals); section (of an organization)
. ■ ■■ ■■■.. ■■ ■
medical department; internal medicine, general practice
surgical department, surgery
,: 「冷;
science
the scientific method
scientist
the natural sciences '
the social sciences applied science
8.毕(勤bl
*
9 .庆(废)qlng
guóqìng(jié)
BF: finish, complete
VO: graduate (lit. complete one1s major work)
BF: blessings, good fortune; to celebrate or congratulate
N: National Day (October first)
10.码 mW
BF: counter (cf. Latin 1 calculus1); numeral, symbol, code; wharf
N: wharf, dock, pier
N: number
V: fly
N: airplane (M: 架 )
N: airport, airfield
12
a9 ay a9 a
Ex: interjection or final particle
nín hao a*
búyao wangle a
。何,你说什么 a, ni shuo shénme
8邑战碗I自3 a,僦5 míngbaile
How are you doing!
Don1t forget, now!
What? What did you say?
Oh, now I understand!
Translations of the Usage Examples
a. Although the United States and China are both republics, they are quite different.
1. There1s a map of the People * s Republic of China in our classroom.
3. There are two black cars in front of the French embassy.
4. Even though we took an express train, we still arrived late.
5. This type of automobile symbolizes Chinese industrial development in recent years.
Hefs going to represent us at the meeting.
6. The Peoplefs Republic of China will hold a reception at the Great Hall of the People to welcome the American cultural delegation.
7. The contents of this science exhibit are extremely good.
9. Friday is National Day, so both workers and students can take the day off.
10. I never can remember his phone number; 11ve dialed the wrong number againl
11. I hear that there1s a MiG-25 at that airport.
“科学讨论会”
语法 Yúfà Grammar
1) “不是…吗” is a kind of rhetorical question used ío confirm a statement. E.g.
你不是会中文吗?请你翻译翻译这个 句子。
你不是看了那个展览会了吗?你给我 介绍介绍吧。
2) Some verb-object constructions can be used as adverbial adjuncts, describing the manners of actions. E.g.
他坐飞机来北京了。
我们用中文讨论问题。
3) If we want to stress the manner, time or place of a completed action, the construction of “是…的"is used, where 是》 can be omitted. If the main verb takes an object, it can be placed after the verb before《的》or after “的》・ E.g・
他(是)坐飞机来的。
你(是)在哪儿学的中文?
我(是)今天早上看见他的。
If there is a directional complement after a V-O construction, «的》is placed at the end of the sentence. E.g.
他上星期到中国去的。
她(是)昨天打电话来的。
The negative form of «是…的》is "不是…的" in which case a是" cannot be omitted. E.g.
他不是去年毕业的。
我不是在这个学校学的中文,是在那 个学校学的。
4) “怎么"and "怎么样" both are interrogative pronouns. “怎么"is used as an adverb, generally in front of a verb, asking about the manner of an action. 怎么样》 is used as an adjective and means the same thing as “怎么" when it precedes a verb. E.g.
这个问题应该蕊样回答?
请你告诉我这个字糕样写。
这本书怎么样?
这本书写得怎么样?
你说说那是怎么样的一本书。
a怎么“ sometimes means the same thing as 口为什么“,but gives a tone of surprise. 怎 么样》has no such meaning. E.g.
他怎么走了?
你怎么不去看电影?
他怎么现在还不回来?
5) The modal particle。吧"sometimes expresses a tone of supposition, often referring to a probability. E.g.
你是昨天来的吧?
你们现在很忙吧?
* 范句 Fànjù Models (-)
L你在中国的 时候,不是 参观了 很多地方吗?你给 我们介绍介绍,怎么样?
2.你的同学 吗?你可以
3.外边不是 到外边去
不是会滑冰 叫他教你。
很暖和吗?我们 走走,好不好?
(二)
4他们坐汽车进城 了。
5.昨天晚上他坐火车到上海 去了。
6•老师用中文 问我们问题, 我们也用中文回答。

参观北京汽车制造厂
(三)
7 .他(是)昨天来的。
8 .他(是)跟他朋友一起来 的。
9 .他们(是)坐汽车来的。
10 .我们(是)星期六看的电影。
11 .我(是)从 图书馆借的 字典。
12 .我(是)在书店遇见他的。
13 .我们(是)五点半回学校来 的。
14 .她不是跟工人代表团一起 到中国去的。
15 .他不是昨天进的城。
(四)
16 .他们是怎么到上海去的?
17 .这句话用中文怎么说?
18 .他今天怎么没来办公?
19 .他们怎么都出去 了?
(五)
2。.今天下午有经验交流会吧? 几点钟开始?
2L您在这个工厂工作了很多 年了吧?您介绍的经验非常 好。
22.他在中国学习的时间很 长 了,对中国的情况一定 很 了解吧?
二下课文 Kèwén Text
遇见老朋友
昨天参观机器制造厂的时候, 我遇见了 夏礼。看见他,我非常 高兴,就说:
“夏礼,你好! 没想到在这儿 遇见你 了」
“啊! 你不是高平吗? 你也 到中国来 了!”
“是啊! 你什么时候来的?”
“我是九月二十五号到的上海, 昨天到的 北京。你是来 学习 中文的吗?”
“对了。我是去年十二月来的。 你已经毕业了 吧?是不是已绘 参加工作 了 ?”
“我是去年夏天毕业的,秋天 参加的工作。这次我是跟科学 代表团一起来的。我是翻译了
“你们是怎么来的? 坐火车 来的吗?”
“不,坐飞机来的。我们是来 参加中华人民共和国 国庆活动 的。你今天也是来参观工厂 的吗?”
“是啊!没想到参观工厂的时候 遇见了 老朋友,我太高兴了!你 现在很忙吧?以后有时间一定 要去我们学校玩儿玩儿。”
“好,我一定去!我去的时候 先给你打个电话。”
“好极了! 我的电话号码是 八九,零七四三。”
“好,再见!”
“再见!”
Lesson 16
New Words with Old Characters
・ I我彖gu6jiā
N: country, nation, state
New Characters and Words
1 .刚(制D gang
A: just (a moment ago)
刚才 gǎngcái* 问“前 ganggang*
A: just (a moment ago)
A: just (a moment ago)
2 .向(黝 xiàng
face, look toward, turn to; aim, aspire or strive (in a certain direction) toward
always (never)
learn from the people (lit. look toward the people to study)
何来 xiànglái (bu^-)* 南人民学”涯/in
CV:
MA:
|
3.接 jiē |
V: meet, receive; connect; continue |
|
拣人缘小* |
VO: meet someone (at the station, dock, airport, etc.) |
|
接着mzhe* |
V: go on, continue (where one left off) A: subsequently, immediately thereafter, go on to |
|
才妥电访jiē diànhuà* |
VO: answer the telephone |
4.
阿 qi
精细待 qí zìxíngchē* VO:
5,惯 guan
BF:
习惯 xígu2n*
SV:
N:
ride (bicycle, horse, etc.)
ride a bicycle
accustomed to, comfortable
with, used to; habit
used to, accustomed to habit
6.安 an
一)各彳多小 píngān*
tiananmen
BF• peace, tranquility
IE: bon voyage (lit. may your entire route be smooth and peaceful)
N: Tian An Men (also known as the Gate of Heavenly Peace)
7. guǎng
广告
广扬 火如广抄
guǎnggào*
guǎngchǎng
tiǎnǎnmén guǎngchǎng
SV: broad, expansive
N: advertisement, commercial
N: square (lit. broad field)
Ns Tian An Men Square
8.雄 xióng
BF: masculine, virile, powerful
荚雄 yīngxióng
N: hero
(Note: the character 英 has the meaning of T sublime, noble, eminent.T)
9.纪 jì
BF:
record (in writing); written record; commemorate
纪念支ni2n
commemorate
a鑫晶 jìniànpin
N:
memento, souvenir, keepsakej
10.碑 bēi
N:
inscribed stone tablet, monument
N:
memorial, monument
the Monument to the People1s Heroes (in Tian An Men Square)
A: (preceding 不 0r 没)contrary
11.并(ÉÈsÉÈ) bìng
to what one might expect, in fact, actually
12.且 qiě
BF:
furthermore, moreover
号艮 blngqiě
MA:
moreover, also, for that matter, in fact
不但… búdan..•
Pat t :
not only..., but also...
存且… bìngqiě.・・
13. 播 bo BF: sow, transmit, broadcast
guǎngbo V/N: broadcast
14.闻 wen
闻到 _多”闻
新闻事JL
wéndào* xīnwén* xīnwénxué xinwén shìyè xīnwén
gōngzuozhě
BF: hear; what has been heard, news
V: smell, sniff
RC: smell
N: news
N: (the study of) journalism
N: (the field of) journalism
N: journalist
15.>'m)qiǎn
7^qiánlán*
SV: shallow (lit. or fig.)
N: light blue
十孑处 hǎochu*
huàíchu* chángchu*
短处 duanchu* 处处 chùchù*
用处 ybngchu*
BF: place, point, spot; office
Ní good point, benefit, advantage
N: bad point
N: strong point (of people)
N: shortcoming (of people)
N: everywhere
N: use, usage
17.目 mù
BF: eye; item or topic
N: topic, theme, title
N: items or events on a program; program (radio, TV, theater)
节0单jiémùdān
N: program (list of events, acts, etc.)
播节目 guǎngbo jiémù N:
radio program
密在<
Translations of the Usage Exampl.6s
a. There are now a large number of emerging nations. (or) ...developing countries.
2. This room faces east.
nDo your studies well; aim higher day by day.n (A quotation from Mao Ze-dong commonly found in Chinese primary schools.)
Go west two blocks and youT11 be there.
5. I *ve gotten so used to these clothes I donf t feel like buying new ones.
Ialready quite used to the weather in Peking now.
Late to bed and late to rise——this habit of yours is very bad.
6. There are some large characters on the wall of Tian An Men that read "Long live the People1s Republic of China.n
7. There are lots of people who exercise in Tian An Men Square each morning.
8. Comrade Wang Jin*xi was a labor hero of China.
9. I brought a lot of souvenirs back from China.
10. The memorial in the center of the square is in commemoration of labor heroes.
11. He says it snows all winter in the north, but actually this isn1t the case.
(This may come as a surprise, but) she really doesn't have any 1abor experience to speak of.
12. He1s very industrious in his work, and very enthusiastic as well.
I don't know French, and for that matter I don1t have the least desire to learn it.
He not only teaches English, but also drives a bus at night.
13. You can hear PRC broadcasts on my radio.
14. Any news?
In the evening I regularly listen to the news (broadcast).
That guy with the camera is probably a newsman.
17. The first item on the program was a dance, and the second was a musical performance.
In the United States, there is a very peculiar kind of radio program during the daytime——every few minutes there 1s a soap commercial.


语法 Yfifà Grammar
1) The adverb "刚" indicates the immediate past and must be placed in front of the element which it qualifies. E.g.
我刚写完汉字,还没作练习。
他昨天刚从中国回来。
他刚出去,就下雨了。
2) “以后" can be applied to past events as well as future ones, while “后来》is applied only to the past. E.g.
我本来学英文,二:又学法文了。
后本
现在你学会了查字典,以后就不怕有不 认识的字了。
3) Two other usages of “又》are:
(1) One thing happening after another. E.g.
我昨天看了电影,又买了 一点儿东西。
(2) The second thing contradicting the first. E.g.
他刚出去为什么又回来了? 我想出去,又怕下雨。
1) To show the progressive aspect, “正在正》or 4在》is placed in front of the verb, or «呢“is placed at the end of the sentence. E.g.
我们正在上课。
他在学习,我没有叫他。
我进去的时候,他正听中文广播。 下雨呢,我们不要出去了。
《正在”,《正》or a在》can be used witha呢力at the same time. E・g«
他正在锻炼身体呢。
他在跟一个朋友谈话呢。
他们正在那个机器制造厂参观呢。
The negative form of the progressive aspect is «汉有汽 E.g.
你正在看杂志吗?
没有,我看画报呢。
我没看杂志,我看画报呢。
2) A subject-predicate construction can also be used as the object. E.g.
我希望你跟我一起去。
我觉得他说中文说得非常好。
你知道不知道阿里在哪儿?
3) The construction indicates the immediate future.
So do “快要…了》「快…了”and “就耍…了汽Eg
要上课了,我们到教室里去吧。
快下雨了,我们进去吧。
夏天你就要毕业了吗?
新年快要到了。
Note: (1) No alternative question can be used when asking a question.
(2) «快要......了力 or《快•…••了》 can take no adverbial ad
junct of time in front of it.
Lesson 16A (EC 45)
一、范句 Fànjù Models
㈠
1•夏礼是星期日 刚来学校 的。
2.我刚去送朋友回来。
3.他们刚参观了 工厂,又 去 看电影了。
(二)
4•我本来想去看电影,后来 谢利来找我,我们就一起 去公园了。
,我们本来要去看张老师, 后来下雨 了,我们就没 去。
6 .我们两个人本来 不认识, 来这个学校以后才认识的。
7 .星期三下午本来有两节课, 现在只有一节课了。
(三)
8 .我们给新同学介绍了 学校 的情况,又跟他们一起去 看中国老师。
9 .星期日我想去公园,又想 应该去看同学,后来就去 看同学了。
1。•我想给谢利送书去,又 怕他不在家。
(四)
1L从我们学校向南(边)走, 就到那个工厂 了。
12 .他工作认真努力,我们应该 向他学习。
13 .我向我朋友介绍了北京很 多有名的地方。
二' 课文 Kèwén Text
去车站接朋友
下午我到车站 去接一个 朋友,他 刚 从 我们 国家 来北京。
我本来想骑 自行车去车站, 就决定坐汽车去。
后来又
想应该跟他一起回来,
四点半火车 到了 北京 站。我 朋友刚从火车上下来,我就用 中文对他说:“查利,你好!”
他用英文说:“我不会中文, 你不是知道吗?”
我笑了,就用 英文 对 他 说:“我每天都用 中文谈话, 已经习惯 了。”
我们坐汽车 离开了 北京站。 经过天安门 广场 的时候,我问 查利:“认识这个地方吗?”
他看了看说:“天安门!”
我 说:“对了,是天安门。你看, 那边是人民英雄纪念碑。以后你 有时间,来这儿看看吧!”我又 向他介绍了 北京很多有名的 地方,并且说:“你以后一定有 机会参观的。”
00
7

天安门广场
人民英雄纪念碑

Lesson 16B (EC 46)
—> 范句 Fànjù Models (-)
1.我们正在上课。
2.他们劳动呢。
3.我正在翻译句子呢。
4.他在锻炼身体。
5.我进去 的 时候,她正 给 孩子们讲故事呢。
6.我正找他,他来了!
;(二)
7.你在作练习吗? 没有,我(在)念课文呢。
8.你写汉字呢吗? 我没写汉字,我(正)看书 呢。
(三)
%我看见他从工厂回来 了。
1。•他告诉我电影《红色娘子军》
的内容很好。
.■ :. ■■■■■■■■ ■: ... 」 . ■
1L我希望我们两国人民互相
学习,互相帮助,加强友谊。
(四)
12.要下雪了。
口.天气就要暖和了。
14.他三点钟就要走 了。
6这本中文书你们快学完 了 吗?
16.国庆节快要至I] 了。
二、课文 Kèwén Text 听中文广播
阿里是我的好朋友。我常常 到他宿舍去玩儿。
有一天,我去他那儿,看见 桌子上有一架新收音机,就问:
“这是你新买的吗?”
“是,上星期日刚买的。”
“样子很好看,声音怎么样?”
“声音也不错。”阿里 开开 收音机, 说:“你听,现在正广播中国音乐 呢。北京虽然很远,但是听得很 清楚」
阿里又说:“一会儿就要广播 新闻 了。”
我问:“新闻节目,你能听懂 吗?”
“现在还不能都听懂,因为 我们掌握的词还不多」
我又问他,还广播一些什么 节目,什么时间广播。他告诉我, 每天 晚上 七点钟还广播一些 简单 的小 故事,是 对 孩子们 广播的。因为这些故事内容比较 浅,句子也不太复杂,所以我们 能听懂大概的意思。他说,他 很喜欢听这些小故事。
这时候我们 听见 新闻 节目 开始 了。阿里说:“我们一起听 吧。”
“好」
听完新闻节目,他关上收音机, 又给我讲了讲听广播对学 中文的好处。我觉得他的经验 很好,从 明天 开始,我也 要经常 听中文广播。
APPENDIX I
Character Index by Radical and Stroke Count (Number below character is lesson where introduced)
1 STROKE
义王永农求举溢
一干于专丰互夫且世击死而去
9 24 4 29 11 19 16 18 30 25 28
… .. ... . ..
束求面奏复整
且曲师非果
火午反处冬乐务史失各走去
向杀耒墉禹重复舞靠
国飞发电民既
市产交齐泉变帝灵两毫
/决冰冻介况净
C军农
i订计过让记设论讲访译词该
语误值谈谅 < 调
二干于专互元
+支午方协华克博
厂历万压厚原
匚匹医
卜处
16
||列划创创利刮削制副剥
J 15 23 21 16 7 8 27 5 21 27
门内同周
… 9 4 9
八公并兴
4 16 13
共典单首
3 12 13 5
人介全众合舍命
4化仙代伤伟体份体使佚侬修
I 4 25 15 22 22 4 18 8 14 31 29
侵倒借健
勺包
24
2 28 22 23 29 25
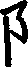
30
力劝力口
2 20 11
务动助努劳勇勤
3 STROKES

汉汗沟汽沙浅油
治注治派海
26 2 7 24 14
涣流消清深渣涨滑湿游满演
21 7 30 7 28 26 29 8 31 30; 31
■ '. ■ ; ■ ■ ■>, ■
灌
29
] 惯
*16
4宁它安灾实室宿寓赛
广庆庄床瘴店度座用鹿
门间闻
£ 迎运违迫适选迷造通魂遍遇
14 24 20 27 18 27 22 5 24 31 12
寸导封
才扔扬脚抢抗抽拔拉拚抬招持
■ . . . . . ■ . , '■
■ .. ■" , ; . ■ ■ . - ■ ■
挖指拼损检换接据推指搜提
25 28 31 26 24 20 16 30 31 21 30
<握搬播操
工贡
23
土 上场幸堂豉墙增
士
22

廿节共苦英草药黄蓝薄藏
3 3 25 1 24 19 4 4 2 30
大夫失奋泰
19 26 29 21
小党堂
27 6
号古史台 3 25 1 28
只另各合吗同0队向
3 21 17 14 1 4 31 16
和呼
1 18
虽
12
响。自
21 20
品
10
。阿售喊嗓
15 18 30 31
团团围困图阅
n 市师希帝格
彳律待
须彩影
…、烈热照热
斗斗
方方
V 6
火火灯灾炼烧
心志急总恩息您感愚慧
户户
19
社视神祝福
王金珍班理挈黎
• 2 30 14 5 24 26 3 2 30 24 21
29
较较辅输辆
29 7 3 22 15
或成 4 21
15
17
风8
5 STROKES
28 19 30 19
17
广病
19
本补被
22
业业
4
目目才目眼
16 11 30
29 6 18 5 13 23
26
“19 1 1 31 6
1 7 1 15 8 10,23 22 25 29
9
l 28
7
6 STROKES
24
I 30 30
米米粮精糖
再取
页须赖领题
竹答筑简
白鱼
5
22
23
28
7 STROKES
口 2;
29
8 STROKES
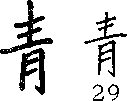
9 STROKES
Q 0
20
30
APPENDIX II
Character Index by Pinyin
|
(Number |
below character is |
lesson where introduced) | |
|
A |
阿 8 |
啊 15 | |
|
AN |
安 16 | ||
|
BA |
爸 23 |
巴 30 | |
|
BAN |
琏 3 |
搬 25 | |
|
BANG |
浜 21 | ||
|
BAO |
簿 2 |
笆 24 | |
|
BE I |
背 7 |
16 24 |
被 27 |
|
BI |
毕 15 |
|
BIAN |
遍变 12 23 |
|
BING |
冰并寂 8 16 19 |
16 20 27
17 20 21
CAN
CANG
CAO
CHA
CHAN
CHANG
CHENG
CHI
CHOU
CHU
14 26
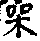
6
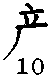
CHUAN
23
|
CHUANG |
床窗创 4 19 21 | ||
|
CHUN |
春 8 | ||
|
CI |
词 | ||
|
1 | |||
|
CUN |
对 26 | ||
|
DA |
答 2 | ||
|
DAI |
待 14 |
代 15 | |
|
DAN |
单 13 | ||
|
DANG |
党 27 | ||
|
DAO |
与蹈倒 3 14 30 | ||
|
DENG |
灯 9 | ||
|
DI |
帝 25 | ||
|
DIAN |
电 6 |
店 6 |
典 12 |
|
DIAO |
调 7 |
.. | |
|
DING |
订 18 |
|
DIU |
去 24 |
|
DONG |
冬动冻 8 10 20 |
|
DOU |
斗 29 |
|
DU |
度 18 |
|
DUAN |
锻斯 6 17 |
|
DUI |
队 26 |
|
EN |
恩 22 |
|
ER |
而 28 |
|
FA |
发 2 |
|
FAN |
翻反 9 13 |
|
FANG |
访 17 |
|
FEI |
非肥飞 7 9 15 |
|
FEN |
份奋 | |||||
|
18 |
29 | |||||
|
FENG |
风A |
封 |
丰 |
锋 | ||
|
8 |
17 |
29 |
31 | |||
|
FU |
辅服大 |
福 |
附 | |||
|
2 |
3 |
11 |
19 |
27 |
31 | |
|
GAI |
该 |
改概溉 | ||||
|
8 |
11 |
12 |
29 | |||
|
GAN |
干 |
敢感赶 | ||||
|
9 |
13 |
14 |
27 | |||
|
GANG |
钢 |
刚 | ||||
|
1 |
16 | |||||
|
GE |
各 |
革 | ||||
|
17 |
20 | |||||
|
GONG |
共 |
公 |
贡 |
< | ||
|
3 |
4 |
29 |
31 | |||
|
GOU | ||||||
|
/习 | ||||||
|
29 | ||||||
|
GU |
故姑 |
古 |
效 | |||
|
13 |
24 |
25 |
31 | |||
|
GUA |
到 | |||||
|
GUAN |
现 |
惯 |
灌 | |||
|
5 |
16 |
2中 | ||||
|
GUANG |
A 厂 | |||||
|
16 | ||||||
GUI
GUO
HAI
HAN
HAO
HE HONG
HOU
HU
HUA
HUAN
HUANG
HUI
|
鬼 30 | ||
|
果 21 | ||
|
海 14 | ||
|
汉 1 口 |
碱 30 豆 |
汗 31 |
|
巧 3 |
冢 22 |
宅 22 |
|
和合 1 14 | ||
|
红 4 | ||
|
厚 2 | ||
|
互 11 |
呼 18 |
r 19 |
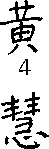
|
HUN |
昏 22 |
|
HUO |
和或泊货 1 4 7 18 |
|
JI |
机记绩纪秋标计既继 5 7 11 16 22 22 28 28 29 集击急 29 30 30 |
4 11 29
|
JIANG |
3 讲 2 |
10 |
13 |
17 |
17 |
24 |
29 |
|
JIAO |
较交 7 11 |
角 18 | |||||
|
JIE |
介 10 |
解 10 |
传 12 |
结 14 |
接 16 |
界 18 27 | |
|
JIN | |||||||
|
JING |
京 5 |
净 19 |
精 23 | ||||
|
JIU |
救究 22 28 | ||||||
|
JU |
举周 14 18 |
剧尾 21 25 |
扰 30 | ||||
JUE
JUN
KANG
KAO
KE
KONG
KU
KUANG
KUN、
KUO
LA
LAN
LAO
15 23
4 责 13
|
LEI |
里而 东田 23 30 |
|
LENG |
金 8 |
|
LI |
历力利立理 1 2 7 17 17 |
|
LIAN |
练炼连 2 6 20 |
|
LIANG |
辆谅董粮冕 15 17 29 29 31 |
|
LIAO |
嚓 31 |
|
LIE |
列烈 15 28 |
|
LIN |
邻 25 |
|
LING |
零另领 2 21 26 |
|
LIU |
留流 5 7 |
|
LOU |
楼 6 |
|
LUN |
论 9 |
|
LÚ |
绿律 4 26 |
|
lUe |
略 13 |
|
MA |
吗褶马蚂 |
|
1 15 20 23 | |
|
MAN |
满 |
|
31 | |
|
MEI |
妖 |
|
27 | |
|
MI |
迷耒 |
|
22 24 | |
|
MIAN |
面 |
|
20 | |
|
MIAO |
蒋 |
|
21 | |
|
MIE |
灭 |
|
30 | |
|
MIN |
民 |
|
3 | |
|
MING |
命 |
|
20 | |
|
MU |
目 |
|
16 | |
|
NEI |
内 |
|
9 | |
|
NIANG |
娘 14 |
NIN
|
1 | |
|
NING |
宁 20 |
|
NONG |
农 23 |
|
NU |
努 2 |
NUAN
|
PA |
爬 23 |
|
PAI |
派 24 |
|
PANG |
e |
|
PEI |
赔配 26 28 |
|
PI |
匹 31 |
|
PIAN |
片 13 |
|
PI AO |
曲 18 |
|
PIN |
品才力拼 10 31 31 |
|
PO |
过 ’27 | |||||
|
Qi |
期 4 |
器 5 |
芥/ 7 15 |
骑 16 |
妻不切 25 31 | |
|
QIAN |
铅 1 |
浅 16 |
歉 26 | |||
|
QIANG |
强 11 |
墙枪抢 23 30 30 | ||||
|
QIAO |
敲 19 | |||||
|
QIE |
且 16 | |||||
|
QIN |
侵 13 |
勤 13 |
琴 21 | |||
|
QING |
、生 7 |
庆 15 |
青 29 |
轻 29 | ||
|
QIU |
秋求 8 22 | |||||
|
QU |
曲 21 |
取 28 | ||||
|
QUAN |
劝 20 |
金 24 | ||||
|
QUE |
确 7 | |||||
|
QUN |
群 30 | |||||
RANG
RE
RENG
RU
SAI
SAN
SE
SHA
SHANG
SHAO
SHE
SHEN
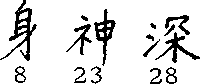
SHENG
|
SHI |
史师室始食实c视世 1 1 3 5 6 10 14 17 18 适士市石失示湿 18 22 24 25 26 31 31 |
|
SHOU |
首熟收售受 5 7 9 18 22 |
|
SHU |
林静於多 |
|
SI |
死 25 |
|
sou |
叟搜 25 30^ |
|
su |
相 4 |
|
SUI |
虽 12 |
|
SUN |
布卜才员 25 26 |
|
TA |
把t 1 25 |
|
TAI |
护台 22 28 |
|
TAN |
谈 13 |
|
TANG |
堂糖躺 6 9 19 |
TAO
TE
TI
TIAN
TIAO
TING
TONG
TOU
TU
TUAN
TUI
WA
WANG
30
|
WEI |
危伟 |
(S尾 |
|
22 22 |
28 30 | |
|
WEN |
闻 16 | |
|
WO |
握 7 | |
|
wu |
午误 |
舞软务 |
|
3 7 |
14 20 26 | |
|
XI |
习析 1 3 |
息希系篇吸 |
|
5 13 20 27 31 | ||
|
XIA | ||
|
XIAN |
险仙 |
献 |
|
22 25 |
29 | |
|
XIANG |
木目向 |
响象 |
|
11 16 |
21 28 | |
|
XIAO |
削消 27 30 | |
|
XIE |
协X 21 22 | |
|
XIN |
f 25 | |
|
|
是兴 |
幸醒 |
|
4 13 |
27 30 | |
|
XIONG |
雄 16 |
益26
义22
医19
帝27
言25
液11
XIU
XU
XUAN
血22
八 3
、、/2
影6K19
27
B 4 812
<4
VĒ^13
YA
YAN
YANG
YAO
YE
YI
YIN
YING
YONG
YOU
YU
YUAN
YUE
YUN
ZA
ZAI
ZAN
ZAO
ZENG
ZHAN
ZHANG
ZHAO
|
ZHE |
渚 A | |||||
|
ZHEN |
珍4t 17 19 | |||||
|
ZHENG |
整争 7 21 | |||||
|
ZHI |
枝 2 |
士 心 2 |
只制支结 3 5 18 25 |
/D 26 |
指 28 | |
|
ZHONG |
种 10,23 |
Í 22 |
终众 24 30 | |||
|
ZHOU |
周 9 | |||||
|
ZHU |
注 2 |
孕 |
之2 2 凫7 、孑1 |
23 | ||
|
ZHUAN |
专 4 |
转稳 30 31 | ||||
|
ZHUANG |
装庄 24 29 | |||||
|
ZONG |
甘、 心 28 | |||||
|
ZOU |
奏 21 | |||||
|
zuo |
座 6 | |||||
APPENDIX III
VOCABULARY INDEX
Part I
Required Vocabulary
APPENDIX III
Index of Required Vocabulary
|
阿 |
-• a |
A BF: |
|
阿里 |
all |
N: |
|
啊 |
a,a, a, a . |
Ex: |
|
爱人 |
àiren |
N: |
|
爰 |
an |
BF: |
|
旦 | ||
|
M整 |
bādian zheng* | |
|
班 |
ban |
n/m: |
室校 公公第助 办办办帮薄碑
|
bangong* |
VO: |
|
bàngongshì |
N: |
|
ban xuéxiào |
VO: |
|
bāngzhu* |
V: |
|
N: | |
|
báo |
SV: |
|
běi |
N: |
běijǐng
beijīng zhoubào
(used in transliterating 8 the sound 1 a1 in foreign languages)
particle
8:00 sharp, 8:00 on the dot 7
soldiers)
help, assistance
monument
capital)
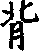
bèi N: back 7
V: turn the back to or on; recite from memory (since recitation was traditionally done with the back turned to the teacher)
直 当 且 但并论<-并搭不不不
|
bèishū* |
VO: |
recite (from a book) from memory |
7 |
|
benzi |
N: |
notebook, exercise book |
1 |
|
bijiao* |
V: A: |
compare comparatively, rather |
7 |
|
bì |
BF.: |
finish, complete |
15 |
|
bìyè* |
VO: |
graduate (lit ・ complete one 1s major work) |
15 |
|
bìxū |
AV: |
must, have to, it1s necessary to |
12 |
|
biān(r) |
BF: |
(localizing suffix) |
6 |
|
biàn |
M: |
time |
12 |
|
bing |
N: |
ice |
8 |
|
bìng |
A: |
(preceding 不 or 没) contrary to what one might expect, in fact, actually |
16 |
|
bìngqie |
MA: |
moreover, also, for that matter, in fact |
16 |
|
bo |
BF: |
sow, transmit, broadcast |
16 |
|
búdàn..* bìngqie... |
Patt: |
not only..., but also... |
16 |
|
búlùn* |
A: |
it doesn't matter, no matter |
9 |
|
bùgandāng^ |
ITm flattered; you1 re too kind |
13 |
|
cai |
BF: multicolored, colored; colors |
14 |
|
càidan(zi)* |
N: menu |
13 |
|
can |
BF: join, participate, take part |
5 |
|
cānguān* |
V: visit (a place), tour |
5 |
|
cānjiā* |
V: join, participate, take 5, part |
11 |
|
cāo |
BF: exercise, drill, train |
6 |
|
cāochang |
N: athletic field, playground |
6 |
|
chá |
V: investigate, check, examine, inspect; look up (in a dictionary) |
12 |
|
chá zìdián |
VO: look up (a word or 12 character) in the dictionary | |
|
chan |
BF: produce |
10 |
|
chanpin. |
N: product |
10 |
|
chángchu* |
N: strong point (of people) |
16 |
|
chang |
N: factory, plant, repair shop |
5 |
|
chang |
BF: field, arena, stage |
6 |
|
chàngpiàn(r)* |
,N: (phonograph) record |
13 |
|
chějiān |
N: workshop, machine shop |
10 |
|
chéng |
SV: okay, satisfactory V: accomplish, become, turn into |
11 |
|
chéng buchéng* |
okay? will it do? |
11 |
|
chéngji |
N: evidence of achievement: grades, scores , marks, results |
11 |
|
chú |
BF: clear |
7 |
f<勃操热查
成匕、 成成
chù chuchù* chuáng chuángdān(zi)* chūn
chūntian* cí ír)
cuòwu
dá
dàgài*
大声把念 大使 大使馆
dàshēngde niàn* dàshi
dàshiguan dài
dai
dàibiào
|
BF: place, point, spot; office |
16 |
|
N: everywhere |
16 |
|
N: bed (M:个长) |
4 |
|
N: bed sheet 4, |
13 |
|
BF: spring |
8 |
|
N: spring |
8 |
|
N: word, term, expression (vs. , single character) |
1 |
|
N: mistake (like 4卷) |
7 |
|
D | |
|
BF: answer, reply, respond |
2 |
|
A: in general terms, approximately, probably |
12 |
|
read aloud |
7 |
|
N: ambassador |
14 |
|
N: embassy |
14 |
|
V: treat BF: serve, wait upon; treatment |
14 |
|
BF: substitute for, take the place of j act on behalf of |
15 |
|
V: represent, speak for, |
15 |
stand for
dàibiaotuán
dan
dānzi*
dànshi
N: representative, delegate
|
N: |
delegation |
15 |
|
ÍF: |
single, singlular; odd (number); list; bed sheet |
13 |
|
N: |
list; bed sheet |
13 |
|
A: |
but |
7 |
|
dao |
BF: lead, guide |
3 |
|
dao |
BF: trample, stamp, tap |
14 |
|
de |
P: (adverbial :deT) |
7 |
|
dēng |
N: lamp, lantern, light |
9 |
|
dìyīkè* |
lesson one, the first lesson |
1 |
|
dìtu |
N: map |
4 |
|
dian |
BF: classic model, canon, code |
12 |
|
diàn |
BF: store, shop, inn |
ó |
|
diàn |
N: electricity |
6 |
|
diànbào* |
N: telegraph, telegram |
6 |
|
diànchě* |
N: trolley car |
6 |
|
diàndēng* |
N: electric light, nthe lights |
n 9 |
|
diànhuà* |
N: telephone, phone call |
6 |
|
diànliú |
N: (electric) current |
7 |
|
diànmén* |
b: electric switch |
6 |
|
diànyīng(r)* |
N: movie, motion picture |
6 |
|
diànyingjī |
N: movie projector |
8 |
|
diào |
BF: tune, melody |
7 |
|
dong |
BF: winter |
8 |
|
dongtian* |
N: winter |
8 |
|
dongjīng |
N: Tokyo (lit. eastern capital) |
5 |
|
dong |
V:, move, touch |
10 |
|
dòngbuliao* |
RC: can.11 move |
10 |
|
dòngshēn* |
VO: start on a journey |
10 |
课 导陷比灯瓢
机 图 报车灯诘流门影影 天呆 圮典店电电电电电电电电起调冬冬东
了 不 动动动
|
短处 |
duanchu* |
N: shortcoming (of people) |
16 | |
|
锻 |
duàn |
BF: forge |
6 | |
|
duànliàn |
V: temper, steel (either lit. or fig.); do physical training |
6 | ||
|
锻炼身体 |
duànliàn |
shēnti |
VO: do physical training (lit. temper the body) |
6 |
|
锻燎思想 |
duànliàn |
sixiang |
VO: temper onef s thought (by reading works of Mao, doing labor, etc.) |
6 |
|
E | ||||
|
二楼 |
èrlóu |
N: second floor |
6 | |
|
F | ||||
|
发 |
fa |
V: issue, emit, send, shoot |
2 | |
|
发生 |
fāshēng |
V: occur, develop, happen |
11 | |
|
发音 |
fayin* |
VO: pronounce N: pronunciation |
2 | |
|
媒 |
fāzhan |
V: develop, expand, grow N: development, expansion, growth |
8 | |
|
翻 |
fan |
V: flip over, turn over; translate |
9 | |
|
翻成汉语 |
fānchéng |
hànyu* |
translate into Chinese |
11 |
|
翱成美文 |
fānchéng yingwén* translate into English |
9 | ||
|
翻跟失 |
fan gēntou |
VO: turn a somersault |
9 | |
|
翻译 |
fānyì* |
V: translate, interpret N: translator, interpreter; translation |
9 | |
|
反 |
fan |
V: turn over, reverse; turn against, rebel; be against, oppose, resist |
13 |
|
反对 |
fanduì |
V: be against, be opposed to; go against, oppose; object to |
13 |
|
反正 |
fanzhèng* |
MA: anyway, in any case, in any event |
13 |
|
雌 |
fàndiàn* |
N: hotel, restaurant, inn |
6 |
|
fanting* |
N: dining room |
14 | |
|
方法 |
fāngfa |
N: method, way, approach |
7 |
|
非 |
fei |
0 BF: not (opposite of ); wrong |
7 |
|
非常 |
f ēicháng* |
A: unusually, extraordinarily, extremely |
7 |
|
非去不可 |
fēi qù bùke* |
must go; insist on going |
7 |
|
飞 |
fēi |
V: fly |
15 |
|
飞机 |
fēiji* |
N: airplane (M: ) 5, |
15 |
|
飞机场 |
fēijichang* |
N: airport, airfield 6, |
15 |
|
肥 |
féi |
BF: fat (of animals); fertile (of land); fertilizer |
9 |
|
肥皂 |
feizao |
N: soap (M:)夫 bar) |
9 |
|
分荀 一. |
fěnxi |
V: analyze N: analysis |
3 |
|
风 |
fěng |
N: wind, breeze |
8 |
|
服 |
fú |
BF: clothes; yield, submit; force into submission, overcome |
11 |
|
辅 |
fǔ |
BF: helpj support, aid |
3 |
|
辅导 |
fúdao |
V: coach |
3 |
|
fù |
BF: return, repeat, review, |
2 |
revive,-restore, renew; multiple, complex
|
fùxí |
V: |
review |
2 |
|
fùzá* |
SV: |
complicated, complex |
2 |
|
匚・ |
G | ||
|
gai |
A: |
should, ought to; itTs time to...; it1s ——1s turn |
8 |
|
gāi shéi. le* |
Whose turn is it? |
8 | |
|
gāi zou le* |
It1s time to go. |
8 | |
|
:gai |
V: |
change, alter, correct |
11 |
|
gaibuliao* |
RC: |
can’t change, canT t be |
11 |
|
gaideliao* |
RC: |
can change, can be altered |
11 |
|
gáihao(le)* |
RC: |
correct(ed) |
11 |
|
gaihuài(le)* |
RC: |
change(d) for the worse |
11 |
|
gai yīfu* |
VO: |
alter clothing |
11 |
|
gaizhèng |
V: |
correct, amend |
11 |
|
N: |
correction, amendment | ||
|
gài |
BF: |
general, overall, on the whole |
12 |
|
gān |
SV: |
dry |
9 |
|
gan |
A: |
dare, venture, be so bold as to |
13 |
|
gan |
BF: |
be moved or touched, feel; feeling, emotion, sensation |
14 |
|
ganxiáng |
N: |
thoughts, feelings, reactions (to an event) |
14 |
|
gan |
V: |
do, be engaged or involved in |
9 |
|
gànmá |
What are you up to?? What are you doing? |
9 | |
|
gàn shénme |
What are you up to?, What |
9 |
are you doing?
习荣 复复
了 3 了 了 t*—> 3 谁走,不得好坏木卫 该该该改改改改改改改
想' 干政感感干
|
钢 |
gang |
N: steel |
1 |
|
gāngbī* |
N: pen |
1 | |
|
刚L |
gang |
A: just (a moment ago) |
16 |
|
刚才 |
gāngcái* |
A: just (a moment ago) |
16 |
|
刚刚 |
ganggang* |
A: just (a moment ago) |
16 |
|
嗡wL 同八 |
gǎoxìng* |
SV: happy, glad A: happily, gladly |
13 |
|
局(兴陟也例Cg五oxingde zuò* |
do gladly |
7 | |
|
跟X借 |
gen X jiè* |
borrow from X |
12 |
|
公 |
gong |
BF: public; office, official duties |
4 |
|
公关洗车 |
gonggòng qìchě* |
N: bus |
4,15 |
|
如土 |
gongshè |
N: commune |
6 |
|
公国 |
gongyuan* |
N: park (lit. public gardens) 6 | |
|
于l |
gongchǎng 、 |
N- factory |
5 |
|
工人卬 |
gǒngrén |
N- worker |
9 |
|
工业 |
gongyè |
N: industry Att: industrial |
8 |
|
X41 工柞条件 |
gongzuò |
V/N: work |
3 |
|
gǒngzuò t i áo j i an |
N: working conditions |
10 | |
|
共 |
gòng |
BF: altogether, share |
3 |
|
共和国 |
gònghéguó |
N: republic |
15 |
|
故 |
gù |
BF: accidental; old; purposeful |
13 |
|
故事 |
gùshi* |
N: story |
13 |
|
guā |
V: |
blow (of wind) |
8 |
|
guāfeng* |
VO: |
wind blows |
8 |
|
guan |
BF: |
observe; view |
5 |
|
guan |
BF: |
accustomed to, comfortable with, used to; habit |
16 |
|
guǎng |
SV: |
broad, expansive |
16 |
|
guángbō |
v/n: |
broadcast |
16 |
|
guǎngcháng |
N: |
square (lit. broad field) |
16 |
|
guànggào* |
N: |
advertisement, commercial |
16 |
|
guójiā |
N: |
country, nation, state |
16 |
|
guóqìng(jié) |
N: |
National Day (October first) |
15 |
|
H | |||
|
hài |
N: |
sea |
14 |
|
han |
BF: |
China, Chinese (from the Han Dynasty -- 206 B・C・ to 220 A・D・) |
1 |
|
hànyú |
N: |
Chinese, the Chinese language |
2 |
|
hànzì |
N: |
Chinese character(s) |
1 |
|
hàochu* |
N: |
good point, benefit, advantage |
16 |
|
hào |
M: |
number (#), day of the month |
3 |
|
hàoma |
N: |
number |
15 |
|
hé |
CV: |
and, with (like f艮) |
1 |
|
he |
V: |
combine, bring together, join |
14 |
JJX❷F<场告琢欣 专刮观惯广广广广国国
语字处 由 海汉汉汉却号卷加合
|
红 |
hong |
SV: red |
4 |
|
名工火 己 hóngdēngjì 红色娘子军^tizijnn |
N: Account (record, tale, etc.) of the Red Lantern N: Red Detachment of Women |
9 14 | |
|
厚 |
hòu |
SV: thick |
2 |
|
£边 |
hòubiān(r) |
N- rear, in back, behind |
6 |
|
互 |
hù |
BF: mutual, reciprocal |
11 |
|
互相 |
hùxiǎng |
A: mutually, reciprocally, one to another |
11 |
|
滑 |
huá |
V: slip, slide, glide; skate ski SV: slippery (either lit. or |
;8 fig.) |
|
滑冰 |
huábīng |
VO: ice-skate |
8 |
|
加水 |
huáshuí |
VO: water-ski |
8 |
|
huáxuě |
VO: ski (on snow) |
8 | |
|
华 |
huá |
BF: brilliant, splendid, glorious; China, Chinese |
15 |
|
化 |
hua |
BF: change, transform; transformation; civilization, culture |
4 |
|
化学 |
huàxué |
N- chemistry Att í chemical |
4 |
|
坏处 |
huàichu* |
N: bad point |
16 |
|
欢迎 |
huǎnyíng* |
V: welcome |
14 |
|
huáng |
SV: yellow, brown |
4 | |
|
回答 |
huídá* |
V/Ní answer |
2 |
|
殆 |
huó |
V: be alive, live |
7 |
|
玷不了 |
huóbuliǎo* |
RC: unable to live |
7 |
|
沽动 |
huódòng |
N: activity Att i active, moving, movable |
10 |
|
活过来 |
huóguolai* |
RC: come to |
7 |
|
殆着 |
huózhe* |
V: alive, living |
7 |
|
或 |
huò |
BF: or |
4 |
|
或是 |
huòshi* |
MA: or |
4 |
|
或渚 |
huòzhe |
MA: or |
4 |
|
J | |||
|
机 |
jī |
BF:machine; opportunity |
5 |
|
机衾 |
jīhui* |
N: opportunity |
5 |
|
机器 |
jǐqi |
N: machine, piece of machinery; 5 engine; radio set (M: | |
|
绿 |
jī |
BF: merit, achievement |
11 |
|
磔身子 |
jīzuò fángzi |
several houses or buildings |
6 |
|
记 |
j % |
¥• note (either in writing or mentally); jot down, record; remember |
7 |
|
记得 |
jìde* |
V: remember |
7 |
|
jlzhě |
N: reporter (lit one who records) |
7 | |
|
jìzhe* |
V: keep in mind, remember |
7 | |
|
记住 |
jìzhù* |
RC: fix in one 1s mind, remember well |
7 |
|
纪 |
j ì |
BF• record (in writing); written record; commemorate |
7 |
|
纪念 |
jìniàn |
V- commemorate |
16 |
|
纪念碑 |
jìniànběi |
•N: memorial, monument |
16 |
|
家 |
jiǎ |
|
加 |
jiā |
|
力噫来 |
jiāqilai* |
|
加强 |
jiāqiáng |
|
加上 |
jiǎshang* |
|
力曜一超 |
jiǎ zài y |
|
架 |
Jia |
|
架子 |
jiazi* |
|
河 |
jiān |
3
单直
jian jiandān* jianzhííde)* jiàn
jiS,ng jiǎnghuà* jiao jiǎo(gěi)* jiāogěi ta*
|
BF: |
(suffix for professionals and specialists) |
4 |
|
V: |
add, increase |
11 |
|
RC: |
add up |
11 |
|
V: |
strengthen, intensify, increase, build up |
11 |
|
RC: |
add up, plus |
11 |
|
add together |
11 | |
|
BF: |
framework, structure, shelf, rack |
4 |
|
,M: |
aircraf19 machine, radio, etc. | |
|
N: |
rack, shelf |
4 |
|
M: |
room |
3 |
|
BF: |
juncture, interstice; middle or midst of; among, between | |
|
BF: |
simple |
13 |
|
SV: |
simple |
13 |
|
A: |
simply |
13 |
|
BF: |
implement, execute, fulfill |
10 |
|
V: |
explain; speak, talk |
2 |
|
VO: |
speak, talk (likeQ为诘) |
2 |
|
V: |
hand over, deliver |
11 |
|
V: |
hand over to, turn over to |
11 |
|
turn (it) over to him |
11 |
|
交流 |
jiāoliú |
|
交流经验.一.,•.、 jiaoliu jmgyan | |
|
教室 |
jiaoshi |
|
教堂 |
jiàotáng |
|
狡 |
jiao |
|
接 |
jiě |
|
接电诒 |
jiē diànhuà* |
|
我人 |
jiē rén* |
|
接者 |
jiēzhe* |
|
节 |
..z jie |
|
节目 |
jiémù |
|
结 |
Jie |
|
结合 |
jiehe |
|
结婚) |
jiéhūn* |
|
解. |
ji苍 jiějué* |
V: flow back and forth, give 11 and take mutually, interchange
N: crosscurrents, mutual give and take, interchange
|
VOS exchange experience |
11 |
|
N: classroom |
3 |
|
N: church (building) |
6 |
|
BF• compare |
7 |
|
V: meet, receive; connect; continue |
16 |
|
VO: answer the telephone |
16 |
VO: meet someone (at the station, dock, airport,
|
V: A: |
go on, continue (where one left off) subsequently, immediately, thereafter, go on to |
16 |
|
BF: M: |
(bamboo) joint, juncture, festival; section, segment span; regulated, rhythmic; to regulate or restrict class period |
3 |
|
N: |
items or events on a program; program (radio, TV, theater) |
16 |
|
BF: |
tie a knot, connect, unite; make a bond or contract; a bond or knot |
14 |
|
V: |
combine, unite, marry |
14 |
|
VO: |
marry |
14 |
|
V: |
untie, loosen, unbutton |
10 |
|
V: |
settle, resolve, solve |
10 |
|
介 |
,o . % , ,Jie |
BF- go or be between |
10 |
|
介绍 |
jièshao* |
V« introduce |
10 |
|
介绍信一 |
ji爸shaoxin* |
N« letter of introduction |
10 |
|
偌 |
・• q Jie |
V: lend, borrow |
12 |
|
僧冻港 |
jiè dongxi^ |
VO: borrow or lend things |
12 |
|
借给汇. |
jiègěi X* : 「;「 ’ .「 . '■.■■:■ ■■ ■ . |
lend to X |
12 |
|
斤 京 |
1 ■< - -,■■■ ■. ■_ jīn |
catty (about 1 & 1/3 pound) |
Í 9 |
|
Jīng |
BF* capital (of a country) |
5 | |
|
经第 |
jīngcháng ..■--■■■ 一 ■■ ■■ ... 人 |
A: frequently, often, regularly |
11 |
|
« |
o an Q •!. jingyan^ |
N: experience |
11 |
|
举 |
ju - - |
V: raise |
14 |
|
jìíqilai^ |
RC« raise, lift up |
14 | |
|
举行 |
jushóu^- |
-VÓ- , raise oneī s hand |
14 |
|
-V 普 juxmg .. |
V: hold节 have5 take place |
14 | |
|
(a meeting, ceremony9 etc«) | |||
|
决 |
•卡 jue |
BF® decide9 make up one's mind |
11 |
|
决定 |
■Jùédìng^' - ,.;.■•. - - |
,V® decide? resolve ■. .■ - |
11 |
|
决心 |
juéxīn |
V- make up one: s mind? decide; be determined to.. a N: resolve § determination; decision? resolution |
11 |
|
军 |
jun |
N* army; military force |
14 |
|
开单孑 |
kāi dānzi^ |
「K「 VO: make a list |
13 |
|
开始 |
kāishl |
V® start 5, begin |
5 |
|
科 |
kē |
BF: |
class or category; field (of study); branch (of medicine); family (of plants or animals); sectior (of an organization) |
15 i |
|
科学 |
kexué |
N: |
science |
15 |
|
可能 |
kSnéng |
SV: A: |
possible, likely possibly, likely to |
12 |
|
课 |
kè |
N: M: |
class period (M: jié -p ); course (M: mén j[ ) * lesson |
1 |
|
课文 |
kèwén |
N: |
text (of a lesson) |
1 |
|
克 |
kè |
BF: |
adequate, capable; overcome |
11 |
|
克服 |
kèfú |
V: |
overcome, conquer (difficulties) |
11 |
|
防 |
kètlng* |
N: |
living room, parlor |
14 |
|
况 |
kuang |
BF: |
conditions, circumstances, situation |
10 |
|
困 困熠 |
kùn |
BF: SV: |
distress, difficulty, quandry sleepy |
11 |
|
kùnnan |
SV: N: |
difficult, troublesome difficulty, trouble |
11 | |
|
来自 |
láizì |
L V: |
come from |
10 |
|
蓝 |
lán |
SV: |
blue |
4 |
|
láo |
BF: |
labor; hard working |
13 | |
|
务动 |
láodòng |
v/n: |
labor, work |
13 |
|
lSoshi |
N: teacher |
1 |
|
lán |
BF: look over, view, browse |
8 |
|
1苍ng |
SV: cold |
8 |
|
líbiān(r) |
N: inside |
6 |
|
litáng* |
N: auditorium |
6 |
|
11 |
BF: history |
1 |
|
lìshl |
N: history |
1 |
|
11 |
BF: power, force? energy |
2 |
|
lì |
BF: profit, advant age, gain, benefit |
7 |
|
lìyòng |
V: utilize, take advantage of use |
,7 |
|
liàn |
BF: practice, drill, train |
2 |
|
liànxi |
Ví practice, drill, train |
2 |
|
liàn |
BF: smelt |
6 |
|
liàng |
M: vehicle |
15 |
|
liàojiě |
V: ascertain, find out; understand N: understanding |
10 |
|
lie |
BF: line up one after the other M: train |
15 |
|
ling |
Nu: zero BF: fragment, fraction, part |
2 |
|
língqián* |
N: small change |
2 |
|
língsuì* |
SV: sundry, miscellaneous |
2 |
惮、边堂 史 用 省览冷里礼历历力利利
习 解 练练燎辆睛
9H4 歹

|
留 |
liú |
V: keep or set aside (for later use); detain; leave behind; stay (in a place) |
5 |
|
留愈来 |
liúqilai* |
RC: put (it) away |
5 |
|
留例九 |
liúshēngjī* |
N: phonograph |
5 |
|
留条儿 |
liútiáor* |
VO: leave a note or message |
5 |
|
留下 |
liúxia* |
RC: leave (it) here |
5 |
|
留学 |
liúxué |
V: study abroad |
5 |
|
留学生 流 |
liuxuéshēng |
N: overseas students |
5 |
|
liú |
V: flow BF: flow, current |
7 | |
|
流利 |
liulì |
SV: fluent N: fluency |
7 |
|
楼 |
lóu |
N: multistory building M: (floor of a storied building) |
6 |
|
楼上 |
lóushàng* |
N: upstairs |
6 |
|
楼下 |
lóuxià* |
N: downstairs |
6 |
|
论 |
lùn |
BF: discuss or debate (principles) |
9 |
|
璇行团 |
lUxíngtuán* |
N: travel club, tour group |
15 |
|
绿 |
1Ù |
SV: green |
4 |
|
l«è |
BF: seize, take by force M |
13 | |
|
石马 |
mǎ |
BF: counter (cf. Latin T calculusT); numeral9 symbol, code; wharf |
15 |
|
硒去 |
mǎtou* |
N: wharf, dock, pier |
15 |
|
吗 |
ma |
P: (question particle) |
1 |
|
慢慢地叫 |
^mànmānrde chī* |
eat slowly |
7 |
|
民 |
min |
BF: people; citizen |
3 |
|
g |
mù |
BF: eye; item or topic |
16 |
|
哪里 |
náli (náll) |
N N: where (like 明口心) |
4 |
|
那里 |
nàli (nail) |
N: there (like 为p |
4 |
|
那种À |
nàzhSng rén* |
that kind of person |
10 |
|
nánjīng |
N: Nanking (lit. southern capital) |
5 | |
|
内 |
nèi |
BF: inside, interior |
9 |
|
内科 内容 |
nèikē* |
N: medical department; |
15 |
|
nèiróng |
internal medicine, general practice N: content, substance; |
9 | |
|
娘 |
niáng |
contents N: mother |
14 |
|
娘子 |
niángz1 |
N: wife, girl, woman |
14 |
|
您 |
nín |
N: you (polite form) |
1 |
|
您好啊 |
nín háo a* |
How are you doing! |
15 |
|
努 努力 暧 |
nìí |
BF: exert |
2 |
|
niilì |
VO: do one's best, work hard |
2 | |
|
nuSn |
SV: diligent, industrious A: with great effort, industriously SV: warm (of weather) |
8 | |
|
nuǎnhuo* |
SV: (pleasantly) warm |
8 |
|
pang1 |
BF- side, flank; close at hand |
6 |
|
pángbiān(r)* |
N" side y beside 5 alongside |
6 |
|
piàn(r) or piān(r) |
.」■ ■ ■ ■ ■ , ■,'1 ' . N* (thin flat item:) card? film争 record才 tablet (of medicine) |
13 |
|
M: slice (of meat, bread? etc® |
兀 |
tablet (of medicine), exp arise
|
(of forest 9 oceanj etc c) | |
|
pin |
BF: goods? commodities5 10 merchandise |

|
Q | |||
|
qī |
BF: |
period^ time limit or./ duration |
4 |
|
qi |
BF: |
uniform, equal5 even, orderly? neatly arranged^ lined up |
7 |
|
-夕^ qi |
V: |
ride (bicycle? horse9 etc. |
)16 |
|
qí zlxíngchē^ |
VO: |
ride a bicycle |
16 |
|
qjL |
N: |
tool, utensily device |
5 |
|
qì |
BF: |
steam |
15 |
|
qìchē^ |
car ? automobile |
15 | |
|
qìliu |
N: |
(air) current |
.7 |
|
qiān |
NW |
lead |
1. |
|
qiānbī^ |
N: |
pencil |
1 |
|
qiánbiān(r) |
N: |
front 9 in front, before |
6 |
|
qiàn |
;SV» |
shallow (lit. or fig.) |
16 |
|
qianlán^ |
W |
light blue |
16 |
|
qiang |
SV: |
strong, powerful |
11 |
|
qiě |
BF : |
furthermore 9 moreover |
16 |
|
qīn |
BF: |
invade? encroach? trespass |
13 |
Àí
皑 车流 t边蓝 期齐骑骑器汽挖<铅铅前浅浅强且侵
|
侵略 |
qinltíè |
V: invade, aggress upon N: invasion, aggression |
13 |
|
勤 |
qín |
BF: industrious, diligent, |
13 |
|
hard working | |||
|
勤劳 |
qínláo |
N: diligence, hard work SV: diligent, hardworking, |
13 |
|
industrious | |||
|
qīng | |||
|
SV: clear |
7 | ||
|
清楚 |
qingchu* |
SV: clear |
7 |
|
情况 |
qingkuàng |
N: conditions, circumstances, situation |
10 |
|
庆 |
qìng |
BF: blessings, good fortune; |
15 |
|
to celebrate or congratulate | |||
|
秋 |
qiū |
BF: autumn |
8 |
|
秋天 |
qiútian* |
N: autumn |
8 |
|
硫 |
què |
BF: true, real |
7 |
|
R | |||
|
让 |
rang |
V: yield, give in; let, allow; |
14 |
|
have (someone do something) | |||
|
CV: by | |||
|
执 | |||
|
、、八 |
rè |
SV: hot |
8 |
|
热情 |
rèqíng |
SV: warm, ardent, enthusiastic |
14 |
|
N: warmth, ardor, enthusiasm | |||
|
热心 |
rèxīn* |
SV: earnest, ardent, warmhearted |
,8 |
|
enthusiastic, zealous | |||
|
人民 |
rénmín |
N: people |
3 |
|
人民画才版gnmín huàbào |
China Pictorial |
3 | |
|
人部承*盎旷ng |
the Monument to the People fs Heroes (in Tian An |
16 | |
|
Men Square) | |||
|
ÌA■篁 |
rènzhēn |
SV: conscientious, serious |
7 |
|
A: conscientiously, seriously | |||
|
sānnián zheng |
a full 3 years, 3 years exactly |
7 |
|
sè |
BF: color |
14 |
|
、** -secai |
N: color (literal or figurative) |
14 |
|
shāng |
BF: discuss; trade, commerce |
6 |
|
shāngdiàn |
N: store, shop |
6 |
|
shāngliang* |
N: discuss, talk over |
6 |
|
shāngyè |
N: commerce |
6 |
|
shàngbān* |
VO: go to work, go on duty, be at work or on duty |
3 |
|
shàngbiān(r) |
N: top, on top, above |
6 |
|
shanghai |
N: Shanghai |
14 |
|
shàngkè* |
VO: go to class, hold class |
1 |
|
shànglóu* |
VO: go upstairs |
6 |
|
shàngwu* |
N: morning, forenoon |
3 |
|
shào |
BF: connect, continue |
10 |
|
she |
BF: dwelling, hostel |
4 |
|
she |
BF: society, community; association, corporation, agency |
6 |
|
shèhui |
N: society |
6 |
|
shěn |
BF: body |
8 |
|
shēntl* |
N: body, health |
8 |
|
shēng(r) |
N: sound, voice, noise |
7 |
|
shengdiào |
N: tone (of spoken Chinese) |
7 |
|
shēngyin* |
N: sound, voice, noise |
7 |
|
shěngchan |
V: produce |
10 |
N: production
边海诛楼午
L上上上上绍、彳
会依调fF 社身券卡4尸力产生
|
生词 |
shěngcí |
N: |
new word(s), vocabulary (of a lesson) |
|
生活 |
shēnghuó* |
V: |
live, make a living |
|
N: |
livelihood, living, life | ||
|
shēnghuó tiáojiàn N: |
living conditions | ||
|
邢 |
shī |
N: |
teacher; (military) division |
|
shísānhào* |
#13, the thirteenth of the month | ||
BF: eat; food
shítáng N: dining hall, cafeteria
shi BF: true, real, actual
shíjiàn V: put into practice
N: practice Att: practical
|
实车 |
shízài* |
SV: true, real, actual A: truly, really, actually |
|
实在的讨 |
^shízàide shuo* |
to be honest with you, to tell you the truth |
|
时间 |
shíjiān |
N: time |
|
时期 |
shíqi |
N: period (of time) |
|
shi |
BF: history | |
|
始 |
shí |
BF: start, begin |
|
便 |
shí |
BF: foreign emissary |
|
室 |
shi |
BF: room, off ice |
|
收 |
shou |
V: receive, accept, collect |
|
收条 |
shoutiáor* |
N: receipt |
|
收音机 |
shouyīnjī |
N: radio (M: or bù) |
|
首 |
shou |
BF: head; chief, principal |
|
首都 |
shoudú |
N: capital (of a country) |
1
7
10
1
3
6
6
10
10
10
10
8
4
1
5
14
3
9
9
9
5
5
|
帝店 |
shūdiàn |
N: bookstore |
ó |
|
书架孑 |
shūjià(zi)* |
N: bookshelf |
4 |
|
熟 |
shú (shóu) |
SV: ripe; done, cooked; familiar |
7 |
|
熟人 |
shúrén* |
N: acquaintance, casual friend |
7 |
|
树 |
shù |
N: tree |
6 |
|
水流 |
shuīliú |
N: (water) current |
7 |
|
水平 |
shuípíng |
N: level, standard (lit. water level) Att: horizontal |
10 |
|
思想 |
sīxiang |
N: thought, thinking, ideas, ideology |
6 |
四间数式n jiàoshì* sìshēng*
3
four classrooms
N: the four tones
7
|
sù |
BF: spend the night, stay (somewhere) |
4 |
|
sùshè* |
N: dormitory |
4 |
BF: although 12
suī
suīrán
MA: although, even though 12
|
T | ||||
|
处 |
t ā |
N: |
she |
1 |
|
狡 |
tan |
V: |
talk about, discuss |
13 |
|
谈诒 |
tánhuà* |
VO: |
talk, converse |
13 |
|
堂 |
táng |
BF: |
hall, spacious room |
6 |
|
糖 |
tang |
N: |
sugar, candy (M: for piece, fr for catty, 舛 bāo for bag)" J |
9 |
|
讨 |
tao |
V: |
seek, ask for, request, demand |
9 |
|
讨饭 |
taofan |
VO: |
beg (as a means of livelihood) |
9 |
|
讨论 |
taolùn |
V: discuss, debate, N: discussion, debate |
9 |
|
特 |
tè |
BF: special9 peculiar |
12 |
|
特别 |
tèbié* |
SV: special, distinctive, peculiar A: especially, particularly |
12 |
|
题 |
t í |
N: topic, problem |
2 |
|
题目 |
tímu* |
N: topic, theme, title 2, |
16 |
|
提 |
t í |
V: raise, bring up, remind, propose, suggest |
10 |
|
提高 |
tígāo |
RC: raise (standards), heighten (consciousness); improve or develop |
10 |
|
体 |
tl |
BF: body |
8 |
|
天安门 |
tiānānmén |
N: Tian An Men (also known as the Gate of Heavenly Peace) |
16 |
|
天安门 广场 |
tiānāmmén guangchang |
N: Tian An Men Square |
16 |
|
tiáojiàn |
N: conditions, terms |
10 | |
|
万 |
ting |
BF: large room, hall |
14 |
|
同 |
tong |
SV: the same V: in the same (class, group, etc,) |
4 |
|
同班 |
tóngbān* |
VO: be in the same class N: classmate |
4 |
|
同时 |
tóngshí* |
MA: at the same time |
4 |
|
同事 |
tóngshì* |
VO: be a colleague of N: colleague, fellow worker |
4 |
|
同学 |
tóngxué* |
VO: be a schoolmate of N: schoolmate |
4 |
|
同志 |
tóngzhì |
N: comrade |
10 |
|
图 |
tú |
N: diagram, chart, illustration 4 | |
|
国右僭 |
túshūguan* |
N: library |
4 |
|
团 |
tuán |
|
外边 |
wàibiān(r) |
|
外科 |
wàikē* |
|
外文 |
wàiwén |
|
逅 |
wàng |
|
为3 |
wèi(le) |
|
文化 |
wénhuà* |
|
wen |
wù 列题和 f 饭捆蹈 闻问我握握牛彳五舞舞误
wéndao*
wèntí*
wo gan shuo* wò
wòshou
wu
wufan*
,wuba yízi
wú
wudao
|
N: |
group, regiment, corps |
15 |
|
W | ||
|
N: |
outside |
6 |
|
N: |
surgical department, surgery |
15 |
|
N: |
foreign language |
9 |
|
BF: |
look into the distance, look towards, look forward to |
13 |
|
A: |
for, on behalf of, for the sake of, in order to, with a view to, for the purpose of |
11 |
|
N: |
culture |
4 |
|
BF: V: |
hear; what has been heard, news smell, sniff |
16 |
|
RC: |
smell |
16 |
|
N: |
problem, question |
2 |
|
I dare say |
13 | |
|
BF: |
grasp, hold in the hand |
7 |
|
VO: |
shake hands |
14 |
|
BF: |
noon |
3 |
|
N: |
lunch, noon meal |
3 |
|
five chairs |
4 | |
|
BF: |
dance |
14 |
|
N: |
dance, dancing |
14 |
|
BF: |
mistake |
7 |
xi
xī
xī
xíwang* xí
xíguàn*
|
BF: split (wood, etc.); analyze |
3 |
|
BF: breath; stop, rest |
5 |
|
BF: hope |
13 |
|
V/N: hope |
13 |
|
BF: review, practice, study |
1 |
|
SV: used to, accustomed to |
16 |
|
N: habit |
琏边课 下下下
xiàbān* xiàbiān(r) xiàkè*
|
VO: get off work, get off duty 3 | |||||
|
N: |
bottom, |
at |
the bottom, below |
6 | |
|
VO: |
get out class |
of |
class, |
dismiss |
1 |
|
xiàlóu* |
VO: go downstairs 6 | |
|
下午 |
xiawu* |
N: afternoon 3 |
|
下雪 |
xiàxue* |
VO: snow 8 |
|
下雨 |
xiayu* |
VO: rain 8 |
|
xià |
BF: summer 8 | |
|
* 复天 |
xiàtian* |
N: summer 8 |
|
xiang |
BF : reciprocal, mutual, one to 11 | |
|
A。 |
,■ ■■■ -■ |
another |
相当 xiāngdāng* 相互 xiānghù
xiāngxìn
汴目 xiàng
A: fairly, pretty, comparatively 11
A: mutually, reciprocally, 11 one to another
V: believe
N: likeness, picture, photograph
13
xiàngpiàn(r)*
N:
photograph
xiàng
CV:
face, look toward, turn to; aim, aspire or strive (in a certain direction) toward
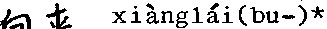
MA: always (never)
16
|
新华字典 |
xīnhuá zìdian |
the New China Dictionary |
15 | |
|
薪阑 |
xínwén* |
N: |
news |
16 |
|
生 |
xíng |
BF: |
star, heavenly body |
4 |
|
星期 |
xīngqī* |
N: |
week |
4 |
|
兴 |
xìng |
BF: |
interest, pleasure, excitement |
13 |
|
雄 |
xióng |
BF: |
masculine, virile, powerful |
16 |
|
休 |
xiū |
BF: |
rest; take a break or vacation; resign |
5 |
|
侪息 |
xiūxi* |
V: |
rest, take a break or vacation |
5 |
|
xū |
BF: |
necessary |
12 | |
|
xuéxí |
V/N: |
study |
1 | |
|
xue |
N: |
snow |
8 | |
|
Y | ||||
|
颜色 |
yánse* |
N: |
color |
14 |
|
验 |
yàn |
BF: |
examine, test |
11 |
|
业 |
yè |
BF: |
calling, trade, occupation, profession |
4 |
|
yīfu* |
N: |
clothes, clothing |
11 | |
|
一遍 |
yíbiàn |
Nu-M: |
once |
12 |
|
-关 |
yígòng* |
A: |
altogether, in all, all told |
3 |
|
一架飞机yí”青fěijí |
one aircraft |
4 | ||
|
píngàn* |
IE: |
bon voyage (lit. may your entire route be smooth |
16 | |
|
and peaceful) | ||||
|
一为 |
yípiàn(r)* |
Nu-M: |
one slice of..., one... tablet, an expanse of... |
13 |
|
yízuò lóu |
a building |
6 |
|
yízuò shān |
a mountain |
6 |
|
V yi |
BF: chair |
4 |
|
yīzi* |
N: chair (M:个^0r f巴) |
4 |
|
% v yiqi |
N: together (like 一,夫儿) |
5 |
|
yìzhāng chuáng* |
one bed |
4 |
|
yìzhí bī* |
a pen |
2 |
|
yìzhī shou* |
one hand |
3 |
|
yì |
BF: translate |
9 |
|
yi |
BF: friendship |
11 |
|
yīn |
N: sound, musical note |
2 |
|
yīnyue |
N: music |
14 |
|
yíng |
BF: sublime, noble, eminent; |
1 |
|
used in transliterating | ||
|
yīngguo* |
N: England |
1 |
|
yingwén* |
N: English (language) |
1 |
|
yīngxióng |
N: hero |
16 |
|
yīngyu |
N: English, the English |
2 |
|
language | ||
|
yīnggāi* |
A: should, ought to |
8 |
|
ying |
BF: meet, welcome, receive |
14 |
|
ylng |
BF: shade, shadow, reflection |
6 |
|
yìngyòng |
V: apply |
14 |
|
N: application | ||
|
A: applied; practical | ||
|
yong |
BF: brave, courageous |
13 |
|
yonggan |
SV: brave, courageous, bold |
13 |
|
yòngchu |
N: use, usage |
16 |
楼山 座座
国文雄语 荚英勇奏
丸 用
应迎影应
敢处 勇勇用
有经验 youjīngyàn* 甯乂经验y* X jfngy^n*
谊」法 引见 友语语雨预预遇遇
子 因
阅园园原原乐
youyì
V yu
yúf a
yu yù yùxí yù yùjian
yuán
yuan yuánzi*
yuan
yuányīn yuè
SV: experienced
VO: have X experience, have experience in X
N: friendship
BF: language
N: grammar
N: rain
BF: beforehand, pre-
V: prepare
BF; meet with
RC: encounter, happen upon, run into, meet (by accident)
SV: round, circular
BF: garden
N: garden
BF: origin, original, originally
N: cause, reason
BF: music
11
11
11
2
2
8
2
2
13
13
8
ó
6
11
11
14
2
2
11
5
9
志%± 杂架在造
BF: random, miscellaneous
|
zázhì* |
N: |
magazine, periodical |
|
zài X shang |
Patt : |
in terms of X, in X, of X |
|
zào |
BF: |
do, create, make, fashion, |
|
build | ||
|
zào |
BF: |
soap |
|
Z (Cont.) | ||||
|
< |
zhan |
BF: |
unfold, unroll, open, expand |
8 |
|
展览 |
zhanlan |
v/n: |
displayj exhibit |
8 |
|
展览我 |
zhanlanhuì |
N: |
exhibition |
8 |
|
掌 孽握 |
zhang |
BF: |
palm of the hand; have in the palm of oneT s hand |
7 |
|
zhangwò |
V: |
take in hand, take charge of, handle, have a grasp on, have mastery of |
7 | |
|
招 |
zhāo |
V: |
wave, beckon; recruit; attract |
14 |
|
招待 |
zhāodài |
V: N: |
entertain, be hospitable to, take care of service9 hospitality |
14 |
|
招待衾 |
zhāodàihuì |
N: |
reception |
14 |
|
貂 |
zhào |
V: |
cast light upon: shine on9 illuminate; reflect light: look at one1s image (as reflected in a mirror), make an image of (on film) |
13 ) |
|
煦片 A . |
zhàopiàn(r) |
N: |
photograph |
13 |
|
时和 |
zhàoxiàng* |
VO: |
take a picture, have one f s picture taken |
13 |
|
照狎机 |
zhàoxiàngjī* |
N: |
camera (M: orbù) |
13 |
|
甫 |
zhě |
BF: |
(as a V or VO suffix) they who, he who, one who; (suffix particle) |
4 |
|
zhèli (zhèlī) |
N: |
here (like 这儿) |
4 | |
|
区”龙 |
zhèyibān* |
this class (shift? squad) |
3 | |
|
整 |
zheng |
BF: |
whole, complete, intact |
7 |
|
整7, |
zheng bādian* |
8:00 sharp, 8:00 on the dot |
7 | |
|
如年 |
zheng sānnián* |
e full 3 years, 3 years exactly |
7 | |
|
整齐 |
zhengqí |
SV: |
neat, orderly, shipshape |
7 |
|
正确 |
zhèngquè |
SV: |
accurate, correct |
7 |
|
枝 |
zhi |
M: |
long thin items |
2 |
|
只 |
zhī |
M: |
one of a pair |
3 |
|
zhī |
BF: |
only |
3 | |
|
只好 |
zhīháo* |
A: |
the best thing to do is. , all one can do is... |
3 |
|
o至 八次 |
zhīyào |
MA: |
if only, provided that, so long as |
13 |
|
只要没有zhly》o méiyou... |
barring..., so long as |
13 | ||
|
there are no... | ||||
|
志 制 |
zhl |
BF: |
remember, record; written record |
2 |
|
zhì |
BF: |
cut out, fashion, |
5 | |
|
manufacture; regulate, fix, limit, control; set of | ||||
|
制造 |
rules, system | |||
|
zhìzào |
V: |
make, manufacture |
5 | |
|
制造厂 |
zhìzàochang |
N: |
manufacturing plant, factory |
5 |
|
中国制前 |
yzhongguó zhìzào |
“made in China" |
5 | |
|
XP 华人^民 zhonghuá rénmín 繇国 gsnghéguó |
the People1s Republic of China |
15 | ||
|
中间 |
zhongjian(r) |
N: |
middle, center, between |
6 |
|
中午 |
zhongwu* |
N: |
noon |
3 |
|
zhong |
M: |
kind, type, sort |
10 | |
|
周 |
zhou |
M: |
cycle |
9 |
|
BF: |
cycle, period; cyclic, periodic | |||
|
周报 |
zhoubào |
N: |
periodical, weekly magazine or journal |
9 |
|
注 |
zhù |
|
注意 |
zhùyì* |
|
注意土匕听zhiiyi.de ting* | |
|
耿 |
zhù |
|
% |
zhuān |
|
考jk. |
zhuānyè |
|
字典 |
zìdian* |
|
霰后 |
zuìhòu |
|
最迩 |
zuìjin |
|
座 |
zuò |
|
座心 |
zuòr* |
|
座位 |
zu owe i* |
BF: concentrate, fix (one 1s 2 eyes or mind) upon
attention 2
attention to
specialize; exclusive, specialized; specialty
N: major field, specialty, 4 profession
N: dictionary (of single 12
characters and their meanings)
N: final, last, ultimate 12
MA: finally, at last,
ultimately
N: in the immediate past or 12 future: recent, most recent, latest; imminent
MA: recently, lately; imminently
M: (large objects such as buildings, cities and mountains)
Part II
Supplementary Vocabulary
|
中可你说什么 & shuo shénme What? What did you say? ‘阿 线明白 j wK niíngbaile Oh, now I understand! |
15 15 | ||
|
B | |||
|
背着 |
bèizhe..• |
behind someone r s back |
7 |
|
不要忘了啊 |
búyào wangle a |
Don1t forget, now! |
15 |
|
C | |||
|
彩色 |
caisè |
N: color |
14 |
|
1 |
\tt: color, in color, colored | ||
|
彩色电影 |
caisè diànyíng |
N: color movie |
14 |
|
词典 |
cidian |
N: dictionary (of characters |
12 |
|
and character combinations | |||
|
——words, phrases, expressions, etc.) | |||
|
D | |||
|
单数 |
dānshù |
N: odd numbers (1, 3, 5, 7, etc.) |
13 |
|
单行道 |
dānxíngdào |
N: one-way street |
13 |
|
杷方电彩 |
dìfang sècai |
N: local color |
14 |
|
电力 |
diànlì |
N: electric power, |
6 |
|
electricity | |||
|
G | |||
|
工作者 |
gongzuòzhe |
N: one who works, worker |
4 |
|
广播抑 |
guangbo jiémù |
N: radio program |
16 |
H
|
海军 |
haijūn |
N: navy; sailor |
14 |
|
汉女词典 |
hàn-yīng cídian N: Chinese-English |
12 | |
|
dictionary | |||
|
互相帮忙 |
hùxiāng bāngmáng help one another |
11 | |
|
画冢 |
huàjia |
N: painter, artist |
4 |
|
化学家 |
huàxuéjiā |
N: chemist |
4 |
|
泮下去 |
huóxiaqu |
RC: go on living, stay alive |
7 |
|
J | |||
|
纪念品 |
jìniànpin |
N: memento9 souvenir, keepsake |
16 |
|
节目单 |
jiémùdān |
N: program (list of events, |
16 |
|
acts, etc.) | |||
|
组湘h的 |
jīn^jishang de |
economic problems, |
11 |
|
向题 |
wentí |
problems in economics | |
|
IB社会 |
jiù shèhui |
N: the old (pre-communist) society |
6 |
|
军人 |
jūnrén |
N: military personnel, |
14 |
|
serviceman v | |||
|
科学方法 |
kēxué fangfa |
K N: the scientific method |
y 15 |
|
科学冢 |
kēxuéjiā |
N: scientist |
15 |
|
L | |||
|
为动节 |
láodòngjié |
N: Labor Day |
13 |
|
彦动力 |
láodonglì |
N: labor force |
13 |
|
恭力人民 |
láodòng rénmín |
N: working people, the |
13 |
|
láodòng |
laboring people N: working conditions |
13 | |
|
2件 |
tiáojiàn | ||
L (Cont.)
laodàniáng
N: old lady
méiyou xíwang
hopeless
qīnlíièzhe
N: invader, aggressor
shèhuì huodong N: shèhuì kéxué N: shèhuishang de huàirén
shèhuì shēnghuó N: shèhuì shíjiàn N: shēnshang N:
g n ó í u p hvl g u n h ē s
彖
品学 契全史
shijiàn huodong N:
shípin N:
shìxuéjiā N:
social activities
the social sciences the bad guys of society, social villains
social life
social practice
on the body, on one1s person
standard of living
practical activities foodstuffs, food products historian

tíchu(lai) RC: bring up, put forward, suggest (an opinion, plan, idea, etc.)
14
13
13
10
15
11
6
10
8
10
10
10
4
10
|
w | |||
|
文 彳匕 交 流^gnhuà. jiàoliú |
N: |
cultural interchange, cultural exchange |
11 |
|
X | |||
|
下月巴xiàféi |
VO: |
fertilize, spread fertilizer |
9 |
|
下 xià juéxīn |
VO: |
make a decision, come to a decision, reach a |
11 |
decision
|
xiàng rénmín xuéxí |
learn from the people (lit, look toward the people to study) |
16 | ||
|
嚼者 |
xīnwén gongzuòzhe |
N: |
journalist |
16 |
|
系斤间事业xínwén shìyè |
N: |
(the field of) journalism |
16 | |
|
新闻学 |
xīnwénxué |
N: |
(the study of) journalism |
16 |
|
星星 |
xīngxing |
N: |
star(s) |
4 |
|
学者 |
xuézhe |
N: |
one who studies, scholar |
4 |
Y
|
“卜内 yīnèi |
N Suff: within (opposite of。卜夕卜)9 | ||
|
音乐会yìnyuèhuì |
N: concert |
14 | |
|
音乐家yìnyuèjià |
N: musician |
14 | |
|
荚汉词典"ng-hàji |
cídian |
N: English-Chinese dictionary |
12 |
|
应用方法yingy3ng |
fāngfa |
N: practical application, practical method |
14 |
|
应用化学yingy协ng |
huàxué |
N: applied chemistry |
14 |
|
应用科学yingybng |
kēxué |
N: applied science |
15 |
Y
|
有决心 |
you juéxin |
be determined to..•, be resolved to... |
11 |
|
you xīwang |
hopeful |
13 | |
|
语法学家 |
yufaxuejia |
N: grammarian |
4 |
Z
|
zài lìshīshang zài shuo yíbiàn |
in history, historically say it again, repeat once |
|
zhenggè(de) BF: the whole..., a whole... | |
|
A: entirely, completely | |
|
zhounián |
M: anniversary |
|
zhuānjiā |
N: specialist, expert |
|
zìrán kēxué |
N: the natural sciences |
|
zuìjin de |
in the very near future |
|
jiānglái | |
|
zuìjin (de) |
latest issue, current |
|
yiqī |
issue (of a periodical) |
|
zuòjiā |
N: writer |
11
12
7
9
4
15
12
12
4
268
GPO 785-001/ 63166